Loggerhead sea turtle
| Loggerhead sea turtle | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Loggerhead sea turtle ( Caretta caretta ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Caretta | ||||||||||||
| Rafinesque , 1814 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Caretta caretta | ||||||||||||
| ( Linnaeus , 1758) |
The loggerhead sea turtle ( Caretta caretta ) is a member of the sea turtle group and is probably the best known and most common of this group. Most of the knowledge about sea turtles in general comes from research on this species.
features
In the Loggerhead the carapace (will carapace ) up to 120 centimeters long. It can weigh up to 110 kilograms. The basic color of the animal is red-brown, adult animals have yellow-brown belly armor. It differs from the hawksbill sea turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata) by having a thicker head with more powerful jaws and five instead of four pairs of ribbed shields.
The males can be recognized by the fact that they have a longer tail and longer, curved claws. Your plastron is a little shorter. Your carapace is more flattened and wider.
A study on loggerhead sea turtles living in the wild revealed indications that the animals of this species have a magnetic sense .
distribution
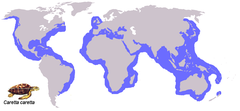
The loggerhead sea turtle is found in all tropical and subtropical seas, including the Mediterranean . The females bury their eggs on sandy beaches, including on Zakynthos in the Bay of Laganas, on Kefalonia on Mounda Beach, as well as in Cyprus in Lara Bay and on the beach of Anamur / southern Turkey. Two subspecies of the species are known, the Caretta caretta caretta and the Caretta caretta gigas . The latter subspecies is native to the Indo-Pacific. Some authors do not consider a distinction between subspecies in the loggerhead sea turtle to be justified.
nutrition
The animals' diet consists mainly of crabs , cephalopods , jellyfish , sea urchins and other animals, but they also eat seaweed . However, hatchlings of their own species have already been found in the stomachs of loggerhead turtles examined.
Reproduction
Mating usually takes place on the surface of the water. The females lay several clutches, each containing between 23 and 178 eggs. The interval between the individual egg-laying is between 12 and 23 days. The eggs are round and have a leather-like shell. The incubation time depends on the ambient temperature and is between 49 and 80 days. The largest known nesting colony of this turtle species can be found on the island of Masirah , which belongs to the Sultanate of Oman . An average of 30,000 loggerhead sea turtles create nesting pits there every year.
Hazard and protection
For their meat, eggs, fat (for cosmetics or as a potential remedy) and tortoise shell , loggerhead turtles were hunted intensely until their populations collapsed. Today both subspecies are threatened with extinction and are under international protection by the Washington Convention on the Protection of Species . At present, the main threat to the animals comes from the trawls of the shrimp fishermen, many of which are killed every year. Internationally, animal rights activists and organizations strive for the survival of the species, among other things by guarding egg-laying beaches such as in Turkey , on Zakynthos (Greece) or in Costa Rica . In 2006, such a program took place for the first time on the 18-kilometer-long coast of Anamur in southern Turkey, and to the surprise of all involved, over 600 clutches were protected. Turtles are also threatened by hunters on the Cape Verde Islands. The Turtle Foundation patrols the nesting beaches to ensure the preservation of the population. In the Messara Bay in southern Crete , a large container port has been threatened since 2006, which is supposed to advance Greece on the way to the transport hub, but threatens the stocks of Caretta caretta . WWF and Schildkrötenschutzbund follow developments on a political level.
The loggerhead sea turtle is listed as a priority species by the European Union in Annexes II and IV of the Habitats Directive and is therefore a species of community interest to be strictly protected, for whose preservation special protected areas must be designated by the member states.
literature
- Indraneil Das: The turtles of the Indian subcontinent. Edition Chimaira, Frankfurt am Main 2001. ISBN 3-930612-35-6
- Caretta caretta in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2006. Posted by: Marine Turtle Specialist Group, 1996. Retrieved on 10 May, 2006.
Web links
- Photos of the loggerhead turtle on www.herp.it
- ARCHELON, the Sea Turtle Protection Society of Greece
- Turtle Foundation
- Meeresmuseum Stralsund - Aquarium with loggerhead turtle
- Project for the protection of sea turtles in Fethiye / Turkey
- Caretta caretta in The Reptile Database
Individual evidence
- ↑ Indraneil Das: The turtles of the Indian subcontinent. Edition Chimaira, Frankfurt am Main 2001, p. 41. ISBN 3-930612-35-6 .
-
^ J. Roger Brothers and Kenneth J. Lohmann: Evidence for Geomagnetic Imprinting and Magnetic Navigation in the Natal Homing of Sea Turtles. In: Current Biology. Volume 25, No. 3, 2015, pp. P392-396, doi: 10.1016 / j.cub.2014.12.035 .
For sea turtles, there's no place like magnetic home. On: eurekalert.org from January 15, 2015. - ↑ Archived copy ( Memento of the original from August 9, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b Indraneil Das: The turtles of the Indian subcontinent. Edition Chimaira, Frankfurt am Main 2001, p. 42. ISBN 3-930612-35-6 .