Urocanase
| Urocanase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Urocanase dimer, Bacillus subtilis | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 676 amino acids | |
| Cofactor | NAD | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | UROC1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 4.2.1.49 , lyase | |
| Response type | Equilibrium reaction | |
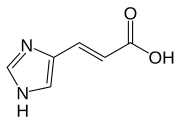
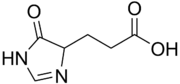
| Substrate | Urocanate + water | |
| Products | Hydroxy imidazole propionate | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 131669 | 243537 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000159650 | ENSMUSG00000034456 |
| UniProt | Q96N76 | Q8VC12 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_144639 | NM_144940 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_65324 | NP_659189 |
| Gene locus | Chr 12: 126.48 - 126.52 Mb | Chr 6: 90.33 - 90.36 Mb |
| PubMed search | 131669 |
243537
|
Urocanase (also urocanate hydratase ) is an enzyme that is involved in the breakdown of the amino acid histidine and catalyzes the second step, the hydration of urocanate to hydroxy-imidazole-propionate . It is found in the liver of vertebrates , but is also found in some bacteria and plants. Mutations in UROC1 - gene , the rare inherited disorder Urocanasemangel cause.
Catalyzed reaction
Urocanic acid (left) is converted into hydroxy-imidazole propionate (right).
construction
Urocanase is a homodimer of 2 * 557 amino acids with a molecular mass of 2 * 61 kDa. Both subunits each contain an NAD + molecule as a fixed, but not covalently bound cofactor . A subunit consists of an NAD + binding domain and a core domain, which also contains the binding site to the other subunit.
literature
- Berg / Tymoczko / Stryer: Biochemistry . 5th edition. Spectrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2003, ISBN 3-8274-1303-6
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt Q96N76
- ↑ Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB): PROSITE documentation PDOC00947. Retrieved September 20, 2011 .