Urolithine
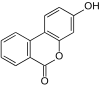
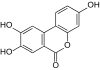
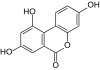
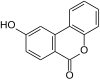
The urolithines are a group of natural phenols that are formed when ellagic acid and ellagitannins are broken down in the digestive tract . Chemically, the urolithines can be described as hydroxylated benzopyran-6-ones .
| Urolithine | |||||||||
| Structural formula |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Surname | Urolithin A | Urolithin B | Urolithin C | Urolithin D | Urolithin M5 | Urolithine M6 | Urolithin M7 | Isourolithin A | Isourolithin B |
| CAS number | 143-70-0 | 1139-83-9 | 165393-06-6 | 131086-98-1 | 91485-02-8 | 1006683-97-1 | 531512-26-2 | 174023-48-4 | 855255-55-9 |
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 8 O 4 | C 13 H 8 O 3 | C 13 H 8 O 5 | C 13 H 8 O 6 | C 13 H 8 O 7 | C 13 H 8 O 6 | C 13 H 8 O 5 | C 13 H 8 O 4 | C 13 H 8 O 3 |
| Molar mass | 228.20 | 212.20 | 244.20 | 260.20 | 276.20 | 260.20 | 244.20 | 228.20 | 212.20 |
Occurrence
Urolithines are not very common in nature. They usually come from plants rich in ellagitannin, such as B. the tamarisk Tamarix nilotica , the pomegranate and in Mumijo .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on Urolithine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 28, 2015.
- ↑ Juan Carlos Espín, Mar Larrosa, María Teresa García-Conesa, Francisco Tomás-Barberán: Biological Significance of Urolithins, the Gut Microbial Ellagic Acid-Derived Metabolites: The Evidence So Far . In: Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine . No. 270418 , 2013, p. 1–15 , doi : 10.1155 / 2013/270418 (English, PDF ).
