VY Canis Majoris
|
Star VY Canis Majoris |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
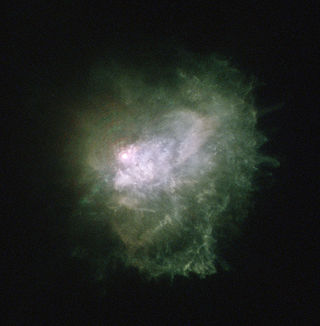
| Image of the star and the surrounding gas cloud with the Hubble Space Telescope | |||||||||||||
| AladinLite | |||||||||||||
|
Observation dates equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|||||||||||||
| Constellation | Big dog | ||||||||||||
| Right ascension | 07 h 22 m 58.33 s | ||||||||||||
| declination | −25 ° 46 ′ 3.2 ″ | ||||||||||||
| Apparent brightness | 8.08 likes | ||||||||||||
| Typing | |||||||||||||
| Spectral class | M3 II / M4 II: | ||||||||||||
| Variable star type | SRc | ||||||||||||
| Astrometry | |||||||||||||
| Radial velocity | +49 km / s | ||||||||||||
| parallax | approx. 0.67 mas | ||||||||||||
| distance | 3,900 ly 1,200 pc |
||||||||||||
| Visual absolute brightness M vis | approx. −3 mag | ||||||||||||
| Proper movement | |||||||||||||
| Rec. Share: | (+5.72 ± 2.01) mas / a | ||||||||||||
| Dec. portion: | (−6.75 ± 4.47) mas / a | ||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||
| Dimensions | 30 to 40 M ☉ | ||||||||||||
| radius | 1420 ± 120 R ☉ | ||||||||||||
| Luminosity |
(430000) L ☉ |
||||||||||||
| Effective temperature | (3600) K | ||||||||||||
|
Other names and catalog entries |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
VY Canis Majoris ( VY CMa ) is a red supergiant . This star is one of the largest stars in the Milky Way , the size of which is known or can be estimated.
properties
In 2006 Roberta M. Humphreys calculated the radius of VY CMa to be 1800 to 2100 times the solar radius (R ☉ ).
More recent studies from 2012 indicate a smaller radius of 1420 ± 120 R ☉ and a closer proximity of 1200 (instead of 1500) parsecs (3900 light years , 37 quadrillion km). If the sun were replaced by such a star, it would expand over the orbit of Jupiter .
There are two different opinions on the assignment of VY CMa: Some researchers (such as Roberta M. Humphreys in her work) believe that the star is a very large and very bright red supergiant . Others (according to the study by Massey, Levesque and Plez), however, come to the conclusion that VY CMa is just a normal red supergiant.
The name part "VY" follows the rules for naming variable stars and states that VY Canis Majoris is the 43rd variable star discovered in the constellation of the Big Dog (Canis Majoris) .
In 2007, American astronomers working with Lucy Ziurys discovered hydrogen cyanide , carbon disulfide , sodium chloride and phosphorus-nitrogen compounds in the vicinity of the star during investigations with a 10-meter radio telescope . This surrounding cloud is also the reason why only a fraction of the visible light emanating from the star arrives on earth and VY CMa therefore appears much darker than would be assumed based on its luminosity .
See also
Web links
- VY Canis Majoris: The Astrophysical Basis of Its Luminosity (English)
- Kastner & Weintraub, HST Imaging of VY CMa (English)
- Entry for VY CMa on daviddarling.info
- Tiny blue dot on YouTube - stars in size comparison
- ESO: Aging Star Weight Loss Secret Reveals November 25, 2015
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Hipparcos catalog (ESA 1997)
- ^ A b c E. De Beck, L. Decin, A. De Koter, K. Justtanont, T. Verhoelst, F. Kemper, KM Menten: Probing the mass-loss history of AGB and red supergiant stars from CO rotational line profiles . II. CO line survey of evolved stars: Derivation of mass-loss rate formulas . In: Astronomy and Astrophysics . 523, 2010, p. A18. arxiv : 1008.1083 . bibcode : 2010A & A ... 523A..18D . doi : 10.1051 / 0004-6361 / 200913771 .
- ↑ roughly estimated based on the apparent brightness and distance
- ↑ Hipparcos catalog (2007)
- ^ M. Wittkowski, PH Hauschildt, B. Arroyo-Torres, JM Marcaide: Fundamental properties and atmospheric structure of the red supergiant VY Canis Majoris based on VLTI / AMBER spectro-interferometry . In: Astronomy & Astrophysics 540, L12 2012, doi : 10.1051 / 0004-6361 / 201219126
- ^ VY Canis Majoris: The Astrophysical Basis of Its Luminosity
- ↑ Bringing VY Canis Majoris Down to Size: An Improved Determination of Its Effective Temperature
- ↑ The dying star as the source of life

