Valine
As Valine firstly summarizes the two isomeric amino acids valine and norvaline together. Both can be understood as propyl substituted glycines. What is striking, however, is isovaline , where a methyl group sits directly on the α- carbon atom .
Valine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids , i. In other words, it is a component of the proteins of living beings and encoded by the genetic code .
If the stereoisomerism is also taken into account, the three D isomers must also be added. They are each described under the associated amino acid articles.
| Valine | |||
| Surname | L - valine | L - Norvaline | L - isovaline |
| other names | ( S ) -2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid, ( S ) -isopropylglycine |
( S ) -2-aminopentanoic acid, ( S ) - n -propylglycine |
( S ) -2-amino-2-methylbutanoic acid, ( S ) -2-amino-2-methylbutyric acid |
| Structural formula |  |
 |
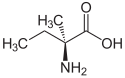
|
| CAS number | 72-18-4 | 6600-40-4 | 595-40-4 |
| PubChem | 6287 | 65098 | 94744 |
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 11 NO 2 | ||
| Molar mass | 117.15 g mol −1 | ||
The Cyclovalin (1-aminocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid) can be considered as a cyclic derivative of Norvalins. It differs from this u. a. by a molar mass lower by two hydrogen atoms (115.13 g · mol −1 ). The defining structural element is a cyclobutane ring. The α-carbon atom is also not a stereocenter; Cyclovaline is therefore not chiral.
See also
literature
- Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer : Biochemistry. 6th edition, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2007, ISBN 978-3-8274-1800-5 . Pp. 697-698, 735, 746.
- Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet: Biochemistry. 4th edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York 2011, ISBN 978-1-11813992-9 . Pp. 68, 70, 80.
- Bruce Alberts , Alexander Johnson, Peter Walter, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts: Molecular Biology of the Cell , 4th Edition, Taylor & Francis 2002, ISBN 978-0-81533218-3 . Chapters I.3 and II.6 (online version).
