Voltage regulator module
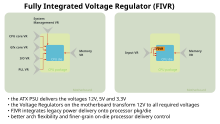
A voltage regulator module ( VRM ; . Dt voltage regulator module), and Point of Load Converter (POL), a voltage regulator, which for example is a microprocessor of a computer with the appropriate operating voltage supplied.
Powerful microprocessors work with the lowest possible voltage to reduce power loss . This low voltage, values in the range around 1 V are common, cannot be made available directly by a remote power supply unit , since the long supply lines with the required operating currents of some 10 A have too high a voltage drop and the voltages on the microprocessor then below the permissible tolerances would decrease.
Therefore, VRMs are in the immediate vicinity of the consumer at the point of load, English point of load , for example on a motherboard . Some VRMs deliver a fixed voltage, but most are able to read the information about the required voltage from the processor. The processor supplies this information to the VRM using what is known as VID (Voltage Identification).
Web links
- intel.com / ... - VRM 9.1 DC-DC Converter Design Guidelines2 (English)
