Sentinel lymph nodes
Guardian lymph nodes , also sentinel lymph nodes , from English. sentinel lymph node (SLN), is a concept in the detection ( diagnosis ) and treatment ( therapy ) of certain malignant tumors ( cancer ), in particular breast cancer ( breast cancer ), black skin cancer ( malignant melanoma ) and prostate cancer (prostate cancer).
In this concept, sentinel lymph nodes are those lymph nodes that are in the first place in the drainage area of the lymphatic fluid of a malignant tumor. If associations of tumor cells have already been carried along with the lymph flow in these lymph nodes, there is a certain probability that further metastases will also be found in the area. If, on the other hand, the sentinel lymph nodes are tumor-free, the likelihood of further lymph node metastases is low . The status of the sentinel lymph nodes (affected or not affected) is therefore of particular importance in the diagnosis and further treatment of these tumors.
execution
The sentinel lymph nodes are identified as part of a lymphatic drainage scintigraphy (sentinel lymph node scintigraphy, sentinel lymph node scintigraphy). To do this, a protein is labeled as a nano- colloid with radioactive 99m technetium and injected into the tumor (intratumorally) or into the tissue near the tumor (peritumorally) ; other possibilities are within the skin (intracutaneously) to the nipple around (periareolar) or in the subcutaneous tissue (subdermally) . The marker spreads via the same lymphatic drainage path as any tumor tissue and accumulates in one or more sentinel lymph nodes. These enrichments are displayed with scintigraphic recordings and with the aid of a measuring probe and marked on the body surface. The number of lymph nodes to be marked varies from case to case.
In the guidelines of this investigation, a reference value of 100–200 MBq 99mTc is recorded for breast cancer , although it can vary depending on the cancer.
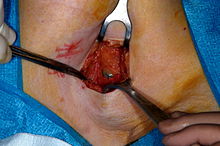
The sentinel lymph node (s) can be surgically removed ( lymphadenectomy ) using the markings and the measuring probe while protecting the other lymph nodes (non-sentinel lymph nodes ). Discoverability of the sentinel lymph node is an intra-operative combination with the dye patent blue V improved. The removed lymph nodes are then processed histopathologically .
meaning
The finding of the sentinel lymph nodes allows further statements to be made about the metastasis of the tumor. If the sentinel lymph node is not affected, it can be assumed with a high degree of probability (in breast cancer in 95% of cases) that the subsequent lymph nodes are also unaffected. In this case, there is no need to remove all the lymph nodes in the armpit ( axillary dissection ). In breast cancer, for example, side effects of lymph node removal such as lymphedema etc. can be prevented. In the rare cases in which there is no sentinel lymph node at all, there is a high probability that the lymphatic system or lymph nodes are tumorous.
literature
- PJ Tanis, OE Nieweg, RA Valdés Olmos, EJ Th Rutgers, BB Kroon: History of sentinel node and validation of the technique. In: Breast Cancer Res. 3, 2001, pp. 109-112, PMID 11250756 </ PMC 139441 < (free full text).
- Heidenreich P et al .: The Sentinel Lymph Node Concept: Status and Clinical Significance. In: Dtsch Arztebl 2001; 98 (9): A-534 / B-434 / C-408
- S1- Guideline for Nuclear Medicine Guardian Lymph Node Diagnostics, procedural instructions for the technical implementation of the German Society for Nuclear Medicine (DGN). In: AWMF online (as of 2014)
Individual evidence
- ↑ , which can be detected via a gamma decay ( technetium-99m decay series ).
- ↑ Renato A. Valdés Olmos et al: Evaluation of Mammary Lymphoscintigraphy by a Single Intratumoral Injection for Sentinel Node Identification In: J Nucl Med 2000; Vol. 41, No. 9, 1500-1506.
- ↑ Ettore Pelosi, MD et al: Sentinel Lymph Node Detection in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Comparison of Periareolar and Subdermal / Peritumoral Injection Techniques In: J Nucl Med 2004; Vol. 45, No. 2, 220-225.
- ↑ H. Wengenmair; J. Kopp; H. Vogt; J. Sciuk: Gamma probes for the intraoperative localization of radioactively marked sentinel lymph nodes, tumors and metastases. Augsburg Hospital, pp. 1–15 .
- ↑ Hsueh EC et al .: Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. In: J Am Coll Surg . 1999; 189: 207-213, PMID 10437844 .
- ↑ Rink T et al .: Lymphoscintigraphic sentinel node imaging and gamma probe detection in breast cancer with Tc-99m nanocolloidal albumin: results of an optimized protocol. In: Clin Nucl Med . 2001; 4: 293-8, PMID 11290886 .