Forest fires in Israel 2016
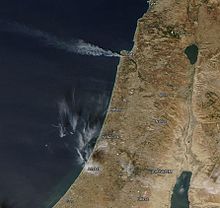
Interpolated and blended satellite image from NASA
Large-scale forest fires in Israel blazed in various parts of the country from November 21, 2016. Several villages in the Haifa region had to be evacuated; 60,000 people were affected.
Background and course
A drought since September 2016 together with dry winds favored the fires. In some cases, temperatures around 30 degrees Celsius still prevailed in November. As with the most devastating forest fires in the history of the State of Israel in 2010, the fires first broke out again in the Carmel Mountains in northern Israel. At times, over 58 sources of fire raged at the same time. In 2010, 44 people died in the fires and numerous were injured.
After the fire disaster in 2010, the fire services in Israel complained that they had too few staff and only outdated equipment. At that time the country did not have a single fire-fighting aircraft. There was widespread public debate and firefighters criticized the Netanyahu government for investing a lot in armaments and little in civil protection . As a consequence, the country bought fire fighting aircraft for 14 million euros and built its own fire fighting aircraft fleet with seven Air Tractor AT-802 machines . The unit was named after Elad Riven , the youngest person to be killed in the 2010 fire in the Carmel Mountains.
There was arson in several places. Israeli police arrested 35 people suspected of having started the fires.
At least 80 people, mostly in the Haifa region, suffered smoking injuries or shock during the course.
affected areas
Haifa region
The region around Haifa in northern Israel and in the Carmel Mountains was particularly hard hit . It was there that the first fire broke out in the historic town of Zichron Ya'akov on the edge of the mountains. Later fires were added in the cities of Nahariya , Harduf, Maʿalot-Tarshiha and Jarka.
Thousands of people in and around Haifa went to safety from November 23rd. In addition, several residential areas in the third largest city in the country were cleared. Around 70,000 people (a quarter of the total population) had been called to evacuate their homes, reported the Haaretz newspaper . On Friday November 25th, most of the fires around Haifa were under control.
Galilee region
The flames threatened a school in Nazareth.
West Bank
Fire also broke out in the West Bank settlements of Dolev , Alfei Menasche and Karnei Schomron. Hundreds of Jewish settlers fled the fires.
Jerusalem region
The village of Nataf on the hills outside Jerusalem had to be completely evacuated. At least three houses burned down.
Fire fighting and rescue work
The National Fire Brigade of Israel ( Sherutei Kaba'ut VeHatzala ) was deployed with units across the country. In addition, units of the army were used to fight fires. Palestinian fire brigade teams arrived in Haifa on November 24th and participated in the extinguishing work with eight vehicles and 40 emergency services.
A total of ten fire-fighting planes from Russia, Turkey , Italy , Greece, France, Spain , Canada and Croatia made their way towards Israel to help with the fire-fighting work. The Republic of Cyprus also sent a fire engine; the country had help u. a. Received by Israel when major fires broke out in the Troodos Mountains . Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu asked Russian President Vladimir Putin for help, who immediately agreed. On Friday evening, November 25, 2016, a Boeing 747-400 , known as a “supertanker”, had been converted into a fire fighting aircraft from the USA . This enabled extinguishing work to be carried out at night.
Reactions
The series of fires developed into a political issue between Israelis and Palestinians. There have been allegations in Israeli media that the fires were started by Palestinians for nationalist reasons; there was occasional talk of a “fire intifada”. Wasel Abu Yussef, a member of the PLO Executive Committee, spoke of baseless and inaccurate allegations that Israeli officials tried to incite the Israeli public against the Palestinians.
According to the Israeli state broadcaster, Prime Minister Netanyahu said that those who deliberately started fires could lose their Israeli citizenship because it was an act of terrorism. Israeli Police Chief Roni Al Sheikh said on November 25, "It is assume that the arson cases were motivated by nationalism. ”The domestic secret service Schin Bet is investigating. Gilad Erdan , Israeli politician and minister of public security, said more than half of the fires were caused by arson.
On November 27, Israel's Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu thanked Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas for Palestinian help in fighting major fires in Israel and the West Bank. Opposition leader Yitzchak Herzog also thanked the Palestinian forces and expressed his conviction that “this tragedy will give rise to a glimmer of hope that things can be different”.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Israel in Flames - The Israel National Trail . In: The Israel National Trail . December 5, 2016 ( israel-trail.com [accessed September 7, 2017]).
- ↑ Israel acquires its own fire fighting planes. In: www.israelnetz.com. Retrieved November 25, 2016 .
- ^ Radio report by ARD correspondent Martin Engelbrecht on December 4, 2010
- ^ Central Council of Jews in Germany Kdö.R .: Israel: Forest fires continue to spread | Jewish general. In: www.juedische-allgemeine.de. Retrieved November 25, 2016 .
- ↑ a b Israel fires: Dozen suspects arrested on suspicion of arson . In: BBC News . November 25, 2016 ( bbc.com [accessed November 25, 2016]).
- ↑ Authorities make fresh arson arrests amid fear of new fires. The Times of Israel, November 27, 2016, accessed November 27, 2016 .
- ↑ SPIEGEL ONLINE, Hamburg Germany: Bush fires in Israel: Tens of thousands of people are supposed to leave their homes. In: SPIEGEL ONLINE. Retrieved November 25, 2016 .
- ^ Two injured as forest fires break out across Israel, approach Jerusalem . In: The Jerusalem Post | JPost.com . ( jpost.com [accessed November 25, 2016]).
- ^ Two injured as forest fires break out across Israel, approach Jerusalem . In: The Jerusalem Post . ( jpost.com [accessed November 25, 2016]).
- ↑ a b c Fighting fires in Israel - Netanyahu thanks Abbas. In: tagesschau.de. Retrieved November 28, 2016 .
- ↑ Fires rage in Zichron Yaakov, Jerusalem-area village Nataf . In: The Times of Israel . ( timesofisrael.com [accessed November 25, 2016]).
- ↑ Fires: Forest fire rages on Cyprus - Israel and Greece send help . In: The time . June 20, 2016, ISSN 0044-2070 ( zeit.de [accessed November 25, 2016]).
- ↑ Ben Ariel: Supertanker arrives in Israel. In: Arutz Sheva . November 25, 2016. Retrieved November 26, 2016 .
- ↑ a b Major fires in Israel: Police arrest twelve people. In: Süddeutsche.de. November 25, 2016, accessed August 26, 2020 .
- ↑ Forest fires in Israel: Turkey supports fire fighting with fire fighting aircraft. In: www.trt.net.tr. TRT German, November 25, 2016, accessed November 25, 2016 .
- ↑ Haifa on fire. ZEIT, November 24, 2016, accessed November 27, 2016 .


