Wangchuck Centennial National Park
| Wangchuck Centennial National Park | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Location: | Bhutan | |
| Surface: | 4914 km² | |
| Founding: | December 12, 2008 | |
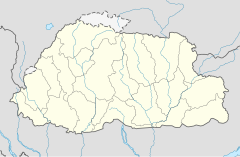
The Wangchuck Centennial National Park is located in the north of Bhuhan and is the largest national park in the country with an area of 4914 km² . It extends over five districts and borders on Tibet to the north and the tributaries of the Wong Chhu (Raidāk) basin in the west . The highest points of the national park are at over 5000 meters .
The national park borders directly on the Jigme Dorji National Park , Bumdeling Wildlife Sanctuary and Thrumshingla National Park in northern Bhutan and in the center of the country on the Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park . Thus almost the entire north of Bhutan is protected by a protection zone made up of national parks.
The following rivers flow through the national park: Puna Tsang Chhu , Mangde Chhu, Chamkhar Chhu and Kuri Chhu.
history
The national park was established on December 12, 2008 in honor of the Wangchuck dynasty, which has existed since 1907.
Flora and fauna
The park is home to over 200 species of vascular plants , 23 species of large mammals, and over 100 species of birds . Notable wildlife species include the Bengal tiger ( Panthera tigris tigris ), snow leopard ( Panthera uncia ), wolf , mishmi-takin ( Budorcas taxicolor ) and the Himalayan black bear ( Ursus thibetanus ).
Individual evidence
- ^ Bhutan Trust Fund. Retrieved September 9, 2017 (American English).