Wnt signal path
| Parent |
| Wnt receptor pathway |
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| QuickGO |
The Wnt signaling pathway is one of many signal transduction pathways through which cells can respond to external signals. The signal path is named after its ligand “Wnt”, a signal protein that, as a local mediator, has an important function in the development of various animal cells. "Wnt" is made up of Wg for Wingless and Int-1 . The term Wingless-type comes from observations with the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster , in which mutations in the wingless - gene lead to a wingless version of the flies. The Int gene promotes the development of breast cancer in mice when its expression is activated by the integration of the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV), a retrovirus near the int1 gene (now Wnt-1).
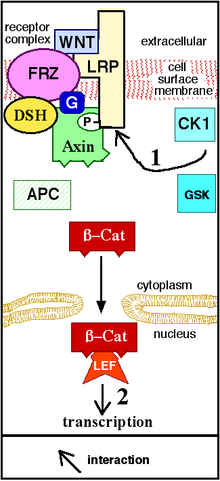
Numerous proteins are involved in the signal transduction of the Wnt signaling pathway . It is essential for normal embryonic development ( embryogenesis ) and is also observed in certain forms of cancer . According to the current state of knowledge, the Wnt signal protein binds to the Frizzled receptor (together with the co-receptor LRP ), which activates the Disheveled protein , which in turn inhibits a protein complex (consisting of GSK-3 β (a kinase ), the tumor suppressor Protein APC and the protein Axin-1 ), which normally degrades β-catenin . Since the degradation of β-catenin is now inhibited, it accumulates in the cytoplasm and in the cell nucleus . In the cell nucleus, the β-catenin forms a protein complex with TCF / LEF and thus activates specific target genes.
Harold Varmus and Roel Nusse played a key role in the discovery and elucidation of the Wnt signaling pathway .
Wnt signaling pathway and APC gene (adenomatous polyposis coli protein)
The APC gene is a tumor suppressor gene that was first found to be mutated in a certain type of colon cancer . However, this gene can also mutate in other types of cancer. The gene codes for the APC protein, which is involved in the degradation of β-catenin in the Wnt signaling pathway.
See also
literature
- B. Alberts et al .: Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2002.
- Logan CY, Nusse R: The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease . (PDF) In: Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol . 20, 2004, pp. 781-810. doi : 10.1146 / annurev.cellbio.20.010403.113126 . PMID 15473860 .
- Kimelman D, Xu W: beta-catenin destruction complex: insights and questions from a structural perspective . In: Oncogene . 25, No. 57, December 2006, pp. 7482-91. doi : 10.1038 / sj.onc.1210055 . PMID 17143292 .
Web links
- Wnt Homepage (English) at Stanford University
- D. Kimelman / reactome: Signaling by Wnt