Deborah Foreman and Eastern box turtle: Difference between pages
this would need to be sourced, WP:BLP |
m Reverted edits by 207.34.120.71 to last version by Soliloquial (HG) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Taxobox |
|||
'''Deborah Lynn Foreman''' (born [[October 12]], [[1962]]) is an [[United States|American]] [[actor|actress]]. She is perhaps best known for her starring role in the 1983 movie ''[[Valley Girl (film)|Valley Girl]]''. |
|||
| name = Box Turtle |
|||
| image = Eastern Box Turtle.jpg |
|||
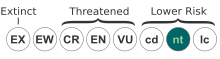
| status = NT | status_system = IUCN2.3 |
|||
| regnum = [[Animal]]ia |
|||
| phylum = [[Chordata]] |
|||
| classis = [[Reptile|Reptilia]] |
|||
| ordo = [[Testudines]] |
|||
| familia = [[Emydidae]] |
|||
| genus = ''[[Terrapene]]'' |
|||
| species = ''[[Terrapene carolina|T. carolina]]'' |
|||
| subspecies = '''''T. c. carolina''''' |
|||
| trinomial = ''Terrapene carolina carolina'' |
|||
| trinomial_authority = [[Carolus Linnaeus|Linnaeus]], 1758 |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Eastern Box Turtle''' (''Terrapene carolina carolina'') is a [[subspecies]] within a group of [[hinge]]-shelled turtles, normally called [[box turtle]]s. ''T. c. carolina'' is native to an eastern part of the [[United States]]. Occasionally, it is referred to as the '''Common Box Turtle''' to distinguish it from the other five subspecies of [[Terrapene carolina|eastern box turtles]]. <ref> {{cite book | last=Carr | first=Archie | authorlink=Archie Carr | title=Handbook of Turtles, The Turtles of the United States, Canada, and Baja Calafornia | origyear=1952 | year=1983 | publisher=Cornell University Press | location=Ithaca, USA | id=ISBN 0-8014-0064-3 | pages=pp 138}}</ref> |
|||
==Biography== |
|||
===Early life=== |
|||
Foreman was born in [[Montebello, California]] to Clyde Foreman, a [[Marine Corps]] [[Aviator|pilot]], and Lynette. She was raised in [[Arizona]] and [[Texas]]. When she was thirteen, her parents enrolled her at the [[Barbizon School of Modeling]] in [[Houston]] to help her overcome shyness, where she received a trophy after completing the courses. In high school, Foreman received high marks and was a [[cheerleader]]. While she was still a student, local photographer Wally Lewis hired her for [[newspaper]] and [[Mail-order catalog|catalog]] ads. A chance meeting with a representative of [[Wilhelmina Models]] led to her signing with their [[California]] office and [[model (person)|modeling]] assignments for [[Maybelline]] cosmetics.<ref>[http://www.deborahforeman.net deborahforeman.net]</ref> |
|||
== |
== Description == |
||
Eastern box turtles have a high, [[dome]]-like [[carapace]] and a hinged [[plastron]] that allows total shell closure. The [[carapace]] can be of variable coloration, but is normally found [[brown]]ish or [[black]] and is accompanied by a [[yellow]]ish or [[orange (color)|orangish]] radiating pattern of lines, spots or blotches. [[Skin]] coloration, like that of the shell, is variable, but is usually brown with some yellow, purplish or [[white]] spots or streaks. This coloration closely mimics that of the winter leaf of the tulip poplar. The color of the shell and skin of an eastern box turtle differs with age; younger turtles of the type are often more vibrantly colored than the older. Furthermore, males normally possess [[red]] [[eye]]s ([[Iris (anatomy)|iris]]es) whereas females usually display brown eyes. Eastern box turtles feature a sharp, horny beak, stout limbs, and their feet are webbed only at the base. Staying small in size, males grow to up to seven inches, and females to about eight. In the wild, box turtles are known to live over 80 years, but in captivity, usually live only between 30-50. Virtually all turtles have a covering of scutes, or modified scales, over the bony shell. The number,size,form,and position of these scutes can help in identifying the turtle. Only in the soft-shelled turtles and leatherback sea turtles are obvious scutes absent, leaving skin to cover the bones. |
|||
[[Image:My Chauffeur.jpg|right|thumb|300px|Deborah Foreman in ''[[My Chauffeur]]'', 1986]] |
|||
[[Image:Eastern box turtle in florida.JPG|thumb|Eastern Box Turtle in Florida|240px]] |
|||
Four weeks after arriving in [[Los Angeles]], Foreman earned her [[Screen Actors Guild|SAG]] card after appearing in a [[McDonald's]] of [[England]] commercial. Resolving to become a serious actress, she took acting lessons from a variety of teachers. Her first acting job was in a comedy pilot for [[NBC]]'s ''[[The Grady Nutt Show]]''. More TV work and two supporting film roles soon followed. After a 1983 appearance on the popular sitcom ''[[Family Ties]]'', her first starring role in a feature film was ''[[Valley Girl (film)|Valley Girl]]'' (1983) with [[Nicolas Cage]], which brought her national fame. |
|||
Eastern box turtles have many uniquely identifying characteristics which separate them from North American [[tortoises]] and water turtles. While the female's [[plastron]] is flat, in males it is concave so the male may fit over the back end of the female's carapace during mating. The front and back of the plastron are connected by a flexible hinge. When in danger, the turtle is able to close the plastron by pulling the hinged sections closely against the carapace, effectively sealing the soft body in bone. The shell is made of bone covered by living vascularized tissue and covered with a layer of [[keratin]]. This shell is connected to the body through its fused rib cage which makes the shell permanently attached and not removable. |
|||
In 1985, Foreman had a small role in the film ''[[Real Genius]]''. In 1986, she was named ''Most Promising New Star'' by [[ShoWest]], the largest and most notable film convention in the world. Foreman's Hollywood career may have stalled at least in part because she was subsequently cast in a string of weakly-scripted and directed comedies. She had a starring role in the 1986 comedy ''[[My Chauffeur]]'', in which she played a somewhat [[Madonna (entertainer)|Madonna]]-influenced character who gets a job as a driver for a stuffy [[Brentwood, Los Angeles, California|Brentwood]] limousine service. However, unlike ''Valley Girl'', the film did not feature elements of dramatic teen angst. ''My Chauffeur'' was widely publicised, but connected only modestly with teen audiences and critics. |
|||
When injured or damaged, the shell has the capacity to regenerate and reform. Granular tissue slowly forms and keratin slowly grows over the damaged area to replace damaged and missing [[scutes]] or [[Scale (zoology)|scales]]. Unlike water turtles such as the native eastern [[painted turtle]] (''Chrysemys picta''), box turtle scutes continue to grow throughout the turtle's life and develop growth rings. Water turtles typically shed their scutes as they grow. |
|||
That same year, Foreman played dual roles in the offbeat dark comedy and preppy murder mystery ''[[April Fool's Day (film)|April Fool's Day]]''. Although her performance was praised by reviewers, the film's plot and surprise ending were widely panned, with critic [[Vincent Canby]] commenting for the [[New York Times]], "... the dialogue is mostly composed of rude variations on ''eek,'' ''ugh'' and ''I'd like to sleep with you this evening.''" |
|||
[[Image:DSCF0100.JPG|thumb|Two Adult Eastern Box Turtles|240px]] |
|||
[[Image:EasternBoxTurtleMale.jpg|thumb|Adult male, Eastern Box Turtle|240px]] |
|||
[[Image:Terrapene carolina carolina young.jpg|thumb|A Young Box Turtle|240px]] [[Image:DSCF0487.JPG|thumb|A tiny hatchling|240px]] |
|||
[[Image:Eastern_box_turtle.JPG|thumb|Tomlinson Run State Park WV|240px]] |
|||
== Distribution & habitat == |
|||
During the five years following, Foreman appeared in over half a dozen low budget [[horror movie]]s and [[independent film]]s. |
|||
The eastern box turtle is found mainly in the eastern United States, as is implied by its name. They are populated as far north as southern |
|||
[[Maine]] and the southern and eastern portions of the [[Michigan]] Upper Peninsula, south to southern [[Florida]] and west to eastern [[Kansas]], [[Oklahoma]], and |
|||
[[Texas]]. The eastern box turtle is considered uncommon to rare in the [[Great Lakes]] region; however, populations can be found in areas not |
|||
bisected by heavily traveled roads. In the [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]], they are a species of Special Interest in [[Ohio]], and of |
|||
Special Concern in [[Michigan]]. |
|||
Eastern box turtles prefer [[deciduous]] or mixed [[forest]]ed regions, with a moderately moist forest floor that has good drainage. They can be also found in open grasslands, or pastures. |
|||
== Behavior & diet == |
|||
===Cult following=== |
|||
The eating habits of eastern box turtles vary greatly due to individual taste, temperature, lighting, and their surrounding environment. |
|||
In the early 2000s, Foreman starred in two independent films and appeared in commercials for [[Chevrolet]]. She enthusiastically participated in retrospective screenings of ''Valley Girl'' and in 2005 taped interviews for nostalgia segments on [[VH-1]], which led to rekindled cult interest in her as the "quintessential 1980s stereotypical female" and new critical appreciation for her acting abilities. Many of her films had already been issued on [[DVD]]. Currently, Foreman owns and operates DF Graphics, an online graphics house. |
|||
Unlike warm-blooded [[animal]]s, their metabolism doesn't drive their appetite, instead, they can just lessen their activity level, retreat into their shells and halt their food intake until better conditions arise. |
|||
In the wild eastern box turtles are opportunistic [[omnivores]] and will feed on a variety of animal and vegetable matter. There are a |
|||
variety of foods which are universally accepted by eastern box turtles, which include [[earthworm]]s, [[snail]]s, [[grub]]s, [[beetle]]s, [[caterpillar]]s, [[grass]]es, fallen [[fruit]], [[berry|berries]], [[mushroom]]s, [[flower]]s, bread, duck weed, and [[carrion]]. |
|||
Studies at [[Jug Bay Wetlands Sanctuary]] in [[Maryland]] have also shown that eastern box turtles have fed on live birds that were trapped in netting. Many times, they will eat an item of food, especially in captivity, just because it looks and smells edible, such as [[hamburger]] or [[egg (food)|eggs]] even though the food may be harmful or unhealthy. Box turtles are also known to have consumed [[poisonous]] fungi making their flesh inedible by native American hunter gatherers. |
|||
Anecdotal evidence suggests that hatchling box turtles are more [[carnivorous]] than their sub adult and adult versions. There is as yet no concrete evidence to support this theory. |
|||
== In captivity == |
|||
Foreman enjoys hand painting furniture and teaches [[yoga]]. She has consistently named ''My Chauffeur'' as her favourite film project, citing that she enjoyed working with the people involved. |
|||
Thousands of box turtles are collected from the wild every year for the domestic [[pet]] trade, especially from Texas, the Carolinas, and |
|||
Arkansas. The eastern box turtle is protected throughout most of its range but many states allow the capture and possession of box turtles for personal use. Although the United States has banned their export, some box turtles still end up in the [[Asian cuisine|Asian]] food market. Captive breeding is fairly commonplace, but not so much that it can supply the market demand. Although box turtles may make hardy captives if their needs are met, and are frequently kept as pets, they are very difficult to keep owing to their many requirements. |
|||
Eastern box turtles require high humidity, warm temperatures with vertical and horizontal [[thermal gradients]], suitable substrate for |
|||
burrowing, and full spectrum [[ultraviolet]] lighting that mimics sunlight. A basking area at one end of the enclosure is important to offer the |
|||
turtle the ability to warm itself and is critical to sexually mature males and females for development of [[sperm]] and [[Ovum|egg follicles]] respectively. |
|||
Eastern box turtles are semi aquatic in the wild and love to immerse themselves completely in water. Therefore, a large, easily accessible |
|||
water dish for bathing and drinking is important to their health. Water should be fresh and clean and available at all times. |
|||
Because box turtles seldom get the nutrients they need to foster shell growth and skeletal and skin development, they also may require vitamin supplements to keep them healthy such as [[calcium]], [[vitamin a]], and [[folic acid]]. |
|||
Captive diets include various live [[invertebrates]] such as [[crickets]], [[worm]]s, [[earthworms]], [[grubs]], [[beetles]] and [[larva]]e, [[cockroach]]es, small [[mice]], and fish (not goldfish). Mixed berries, fruit, [[romaine lettuce]], [[collard greens]], [[dandelion greens]], [[chicory]], [[mushrooms]] and [[clover]] are suitable for box turtles as well. While some high quality, moist dog foods may be occasionally offered, whole animals are preferable. Reptomin is a suitable food for hatchling and immature/subadult box turtles. |
|||
== |
== References == |
||
<references /> |
|||
* When asked by SportsHollywood "What is valley girl Julie Richman doing today?" |
|||
:"Julie won a scholarship to Harvard. Graduated with honors and received another scholarship to Boston University Medical School. Julie became a medical doctor, alas, losing her medical license to a terrible addiction to heroin. As an ex-addict, she now manages Autoworld Go Carts in West Covina, California. She has the highest score on PacMan... Go Julie!!!"<ref>[http://www.sportshollywood.com/askforeman.html Sports Hollywood - Ten Questions with Deborah Foreman<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> |
|||
* "Life is good." |
|||
== External links == |
|||
==Filmography== |
|||
*[http://billsboxturtles.com] Bill's Box Turtles |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
*[http://boxturtlesite.info/diet.html Diet and Feeding Your Box Turtle] |
|||
|- bgcolor="#CCCCCC" |
|||
*[http://herpcenter.ipfw.edu/index.htm?http://herpcenter.ipfw.edu/outreach/accounts/reptiles/turtles/E_Box_Turtle/&2 Center for Reptile and Amphibian Conservation and Management] |
|||
! Year !! Title !! Role |
|||
*[http://www.boxturtle.org] Northern Virginia Reptile Rescue |
|||
|- |
|||
|rowspan="3"| [[1982 in film|1982]] || ''Love in the Present Tense'' || Heather Jenkins |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[I'm Dancing as Fast as I Can (film)|I'm Dancing as Fast as I Can]]'' || Cindy |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''In the Custody of Strangers'' || Karen |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[1983 in film|1983]] || ''[[Valley Girl (film)|Valley Girl]]'' || Julie Richman |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[1985 in film|1985]] || ''[[Real Genius]]'' || Susan Decker |
|||
|- |
|||
|rowspan="4"| [[1986 in film|1986]] || ''Charlie Barnett's Terms of Enrollment'' || Coed/Recruiter |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[My Chauffeur]]'' || Casey Meadows |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[April Fool's Day (film)|April Fool's Day]]'' || Muffy/Buffy St. John |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''3:15'' || Sherry Havilland |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[1987 in film|1987]] || ''Predator: The Concert'' || Park Ranger's Daughter |
|||
|- |
|||
|rowspan="2"| [[1988 in film|1988]] || ''[[Waxwork (1988 film)|Waxwork]]'' || Sarah Brightman |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[Destroyer (film)|Destroyer]]'' || Susan Malone |
|||
|- |
|||
|rowspan="3"| [[1989 in film|1989]] || ''Friends, Lovers, & Lunatics'' ||Annie |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[The Experts (film)|The Experts]]'' || Jill |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[Lobster Man From Mars]]'' || Mary |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[1990 in film|1990]] || ''[[Sundown: The Vampire in Retreat]]'' || Sandy White |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[1991 in film|1991]] || ''Lunatics: A Love Story'' || Nancy |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[2007 in film|2007]] || ''Beautiful Loser'' || Carly |
|||
|} |
|||
[[Category:Turtles]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
[[category:Reptiles of North America]] |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
[[Category:Reptiles of Michigan]] |
|||
[[Category:Fauna of the Eastern United States]] |
|||
[[de:Carolina-Dosenschildkröte]] |
|||
==External links== |
|||
*[http://www.deborahforeman.net/ Official Web Site] (warning, music plays automatically) |
|||
*{{imdb name|id=0286033|name=Deborah Foreman}} |
|||
*[http://www.bippiboy.com/deborah.html A semi-official fan site] |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Foreman, Deborah}} |
|||
[[Category:1962 births]] |
|||
[[Category:American film actors]] |
|||
[[Category:American television actors]] |
|||
[[Category:Living people]] |
|||
[[Category:People from the Greater Los Angeles Area]] |
|||
Revision as of 19:49, 13 October 2008
| Box Turtle | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | T. c. carolina
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Terrapene carolina carolina Linnaeus, 1758
| |
The Eastern Box Turtle (Terrapene carolina carolina) is a subspecies within a group of hinge-shelled turtles, normally called box turtles. T. c. carolina is native to an eastern part of the United States. Occasionally, it is referred to as the Common Box Turtle to distinguish it from the other five subspecies of eastern box turtles. [1]
Description
Eastern box turtles have a high, dome-like carapace and a hinged plastron that allows total shell closure. The carapace can be of variable coloration, but is normally found brownish or black and is accompanied by a yellowish or orangish radiating pattern of lines, spots or blotches. Skin coloration, like that of the shell, is variable, but is usually brown with some yellow, purplish or white spots or streaks. This coloration closely mimics that of the winter leaf of the tulip poplar. The color of the shell and skin of an eastern box turtle differs with age; younger turtles of the type are often more vibrantly colored than the older. Furthermore, males normally possess red eyes (irises) whereas females usually display brown eyes. Eastern box turtles feature a sharp, horny beak, stout limbs, and their feet are webbed only at the base. Staying small in size, males grow to up to seven inches, and females to about eight. In the wild, box turtles are known to live over 80 years, but in captivity, usually live only between 30-50. Virtually all turtles have a covering of scutes, or modified scales, over the bony shell. The number,size,form,and position of these scutes can help in identifying the turtle. Only in the soft-shelled turtles and leatherback sea turtles are obvious scutes absent, leaving skin to cover the bones.

Eastern box turtles have many uniquely identifying characteristics which separate them from North American tortoises and water turtles. While the female's plastron is flat, in males it is concave so the male may fit over the back end of the female's carapace during mating. The front and back of the plastron are connected by a flexible hinge. When in danger, the turtle is able to close the plastron by pulling the hinged sections closely against the carapace, effectively sealing the soft body in bone. The shell is made of bone covered by living vascularized tissue and covered with a layer of keratin. This shell is connected to the body through its fused rib cage which makes the shell permanently attached and not removable.
When injured or damaged, the shell has the capacity to regenerate and reform. Granular tissue slowly forms and keratin slowly grows over the damaged area to replace damaged and missing scutes or scales. Unlike water turtles such as the native eastern painted turtle (Chrysemys picta), box turtle scutes continue to grow throughout the turtle's life and develop growth rings. Water turtles typically shed their scutes as they grow.



Distribution & habitat
The eastern box turtle is found mainly in the eastern United States, as is implied by its name. They are populated as far north as southern Maine and the southern and eastern portions of the Michigan Upper Peninsula, south to southern Florida and west to eastern Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. The eastern box turtle is considered uncommon to rare in the Great Lakes region; however, populations can be found in areas not bisected by heavily traveled roads. In the Midwest, they are a species of Special Interest in Ohio, and of Special Concern in Michigan. Eastern box turtles prefer deciduous or mixed forested regions, with a moderately moist forest floor that has good drainage. They can be also found in open grasslands, or pastures.
Behavior & diet
The eating habits of eastern box turtles vary greatly due to individual taste, temperature, lighting, and their surrounding environment. Unlike warm-blooded animals, their metabolism doesn't drive their appetite, instead, they can just lessen their activity level, retreat into their shells and halt their food intake until better conditions arise. In the wild eastern box turtles are opportunistic omnivores and will feed on a variety of animal and vegetable matter. There are a variety of foods which are universally accepted by eastern box turtles, which include earthworms, snails, grubs, beetles, caterpillars, grasses, fallen fruit, berries, mushrooms, flowers, bread, duck weed, and carrion. Studies at Jug Bay Wetlands Sanctuary in Maryland have also shown that eastern box turtles have fed on live birds that were trapped in netting. Many times, they will eat an item of food, especially in captivity, just because it looks and smells edible, such as hamburger or eggs even though the food may be harmful or unhealthy. Box turtles are also known to have consumed poisonous fungi making their flesh inedible by native American hunter gatherers. Anecdotal evidence suggests that hatchling box turtles are more carnivorous than their sub adult and adult versions. There is as yet no concrete evidence to support this theory.
In captivity
Thousands of box turtles are collected from the wild every year for the domestic pet trade, especially from Texas, the Carolinas, and Arkansas. The eastern box turtle is protected throughout most of its range but many states allow the capture and possession of box turtles for personal use. Although the United States has banned their export, some box turtles still end up in the Asian food market. Captive breeding is fairly commonplace, but not so much that it can supply the market demand. Although box turtles may make hardy captives if their needs are met, and are frequently kept as pets, they are very difficult to keep owing to their many requirements. Eastern box turtles require high humidity, warm temperatures with vertical and horizontal thermal gradients, suitable substrate for burrowing, and full spectrum ultraviolet lighting that mimics sunlight. A basking area at one end of the enclosure is important to offer the turtle the ability to warm itself and is critical to sexually mature males and females for development of sperm and egg follicles respectively. Eastern box turtles are semi aquatic in the wild and love to immerse themselves completely in water. Therefore, a large, easily accessible water dish for bathing and drinking is important to their health. Water should be fresh and clean and available at all times. Because box turtles seldom get the nutrients they need to foster shell growth and skeletal and skin development, they also may require vitamin supplements to keep them healthy such as calcium, vitamin a, and folic acid. Captive diets include various live invertebrates such as crickets, worms, earthworms, grubs, beetles and larvae, cockroaches, small mice, and fish (not goldfish). Mixed berries, fruit, romaine lettuce, collard greens, dandelion greens, chicory, mushrooms and clover are suitable for box turtles as well. While some high quality, moist dog foods may be occasionally offered, whole animals are preferable. Reptomin is a suitable food for hatchling and immature/subadult box turtles.
References
- ^ Carr, Archie (1983) [1952]. Handbook of Turtles, The Turtles of the United States, Canada, and Baja Calafornia. Ithaca, USA: Cornell University Press. pp. pp 138. ISBN 0-8014-0064-3.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help)
External links
- [1] Bill's Box Turtles
- Diet and Feeding Your Box Turtle
- Center for Reptile and Amphibian Conservation and Management
- [2] Northern Virginia Reptile Rescue