Dibromobenzenes
| Dibromobenzenes | |||||||
| Surname | 1,2-dibromobenzene | 1,3-dibromobenzene | 1,4-dibromobenzene | ||||
| other names | o -dibromobenzene | m -dibromobenzene | p -dibromobenzene | ||||
| Structural formula |

|

|
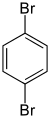
|
||||
| CAS number | 583-53-9 | 108-36-1 | 106-37-6 | ||||
| PubChem | 11414 | 7927 | 7804 | ||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 4 Br 2 | ||||||
| Molar mass | 235.92 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state | liquid | firmly | |||||
| Melting point | 4-6 ° C | −7 ° C | 83-87 ° C | ||||
| boiling point | 224 ° C | 218-219 ° C | 219 ° C | ||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
||||
| H and P phrases | 315-319-335 | 315-319-335 | 315-319-335-400 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | |||||
| 261-305 + 351 + 338 | 261-305 + 351 + 338 | 261-273-305 + 351 + 338 | |||||
In chemistry, the dibromobenzenes form a group of substances consisting of a benzene ring with two bromine atoms (–Br) as substituents . Their different arrangements ( ortho , meta or para ) result in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 6 H 4 Br 2 .
properties
The boiling points of the three isomers are practically the same, while their melting points differ more clearly. 1,4-Dibromobenzene, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point.
presentation
Renewed bromination ( second substitution ) of bromobenzene with bromine and iron (III) bromide results in mixtures of the three isomers, with the meta derivative only being obtained in small quantities. The ortho / meta / para ratio is 13% / 2% / 85%. The dibromobenzenes can be prepared from the phenylenediamines by diazotizing both amino groups and then adding copper (I) bromide ( Sandmeyer reaction ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet 1,2-dibromobenzene from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 13, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c data sheet 1,3-dibromobenzene from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 13, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c data sheet 1,4-dibromobenzene from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 13, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ K. Peter C. Vollhardt , Neil E. Schore: Organische Chemie , 4th edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2005, ISBN 978-3-527-31380-8 , p. 824.
- ^ K. Peter C. Vollhardt , Neil E. Schore: Organische Chemie , 4th edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2005, ISBN 978-3-527-31380-8 , p. 1194.

