2,6-dihydroxyanthraquinone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
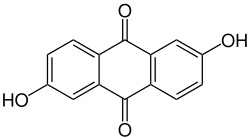
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,6-dihydroxyanthraquinone | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 8 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 240.21 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone , also known as anthraflavic acid , is a natural substance that occurs in madder . It is an organic compound from the substance group of the anthraquinones (more precisely the dihydroxyanthraquinones ).
Occurrence
2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone occurs glycosidically bound together with other anthraquinones in the roots of madder madder .
Extraction and presentation
The 2,6-dihydroxyanthraquinone can be extracted directly from the roots of the madder.
To make anthraflavic acid , methoxybenzoic acid is heated with benzoic acid , concentrated sulfuric acid, and water. This mixture is then boiled with water and then with barite water . By adding hydrochloric acid , the remaining components are precipitated, which are then washed with benzene . Only the anthraflavic acid remains undissolved.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet Anthraflavic Acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 24, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b Carl Liebermann, STV Kostanecki: About the coloring properties and the syntheses of oxyanthraquinones. In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry . 240, 1887, pp. 245-304, doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18872400302 .
- ↑ a b E. Schunk, H. Roemer: Ueber Anthraflavinsäure und Isoanthraflavinsäure. In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . 9, 1876, pp. 379-383, doi : 10.1002 / cber.187600901119 .
- ↑ E. Schunck, H. Römer: Ueber Anthrarufin, a new Bioxyanthraquinone from metaoxybenzoic acid. In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . 11, 1878, pp. 1176-1179, doi : 10.1002 / cber.187801101314 .
- ↑ a b Goverdina CH Derksen, Harm AG Niederländer, Teris A. van Beek: Analysis of anthraquinones in Rubia tinctorum L. by liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array UV and mass spectrometric detection . Journal of Chromatography A , 978, 2002, pp. 119-127, doi : 10.1016 / S0021-9673 (02) 01412-7 .

