G.992.1
The guideline G.992.1 Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) transceivers of the ITU-T describes the bit transmission layer of the interfaces of sending and receiving devices for ADSL over copper wire pairs of telephone networks . As a modulation method is DMT uses - Directive G.992.1 is therefore also G.dmt referred.
G.992.1 specifies various transmission channels in connection with three realizations:
- ADSL and voice services ( POTS ) simultaneously over the same wire pair (in Annex A )
- ADSL and ISDN services simultaneously over the same wire pair (in Annex B )
- ADSL and voice services simultaneously over the same wire pair and with TCM-ISDN (Time Compression Multiplex; in accordance with G.961 Appendix III) in an adjacent wire pair. (in Annex C )
The ADSL described has data transfer rates of around 8 Mbit / s downstream and 1 Mbit / s upstream, depending on the technical design and the environment .
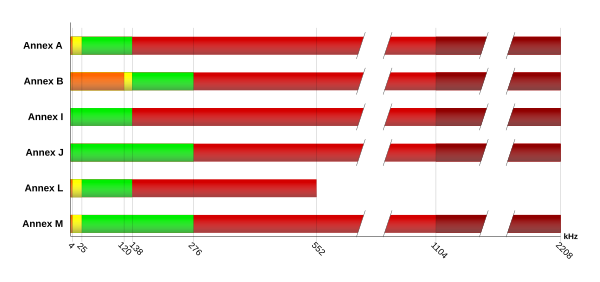
Annex A
The specifications of Annex A ("ADSL over POTS") can only be used for analog telephone connections or pure data connections . A larger frequency range is used for DSL , the range below (below 25 kHz) is still sufficient for analog telephony , but not for ISDN .
Annex A also describes the specification for operation on analog connections and pure data connections for the ADSL further developments ADSL2 / 2 + according to ITU G.992.3 and G.992.5. The frequency range used for the upstream ranges from 25 kHz to 138 kHz for Annex A, the frequencies from 138 kHz to 1.1 MHz (for ADSL2 + up to 2.2 MHz) are used for the downstream.
Annex B
Annex B is designed for digital ISDN telephone connections ("ADSL over ISDN"). ADSL is on a high frequency band , while ISDN or analog signals are transmitted in the area below (both work because this frequency range is wider than in Annex A: the required bandwidth for ISDN is 120 kHz, the bandwidth for analog telephony only up to 3400 Hz ). The upstream range for Annex B is between 138 kHz and 276 kHz, the downstream range between 276 kHz and 1.1 MHz (for ADSL2 + 2.2 MHz).
Annex B also describes the specification for operation on ISDN connections with a restricted DSL frequency band for the ADSL further developments ADSL2 / 2 + according to ITU G.992.3 and G.992.5.
differences
Annex A and Annex B have different physical structures.
By omitting the frequency spectrum with the longest range and the lowest attenuation in Annex B because it is used for the ISDN signals, the range of Annex B is on average ½ km less than in Annex A or the achievable downstream data rate drops by around 1.5 Mbit with the same subscriber line / s or on longer connecting lines with approx. 50 dB line attenuation at 300 kHz up to 1 Mbit / s lower.
The newer, particularly high-range ADSL protocol Reach-Extended-ADSL2 , which, for example, has been used nationwide by France Telecom for long connection lines in France since spring 2006, is also defined exclusively for ADSL-over-POTS. The ADSL2 / 2 + variants according to ITU G.992.3 / 5 Annex M with a higher upstream of up to 3.5 Mbit / s are also not available for ADSL-over-ISDN.
With some DSL modems (e.g. the Fritz! Box 7170 introduced in 2006 ), the annex variant used can be changed by importing different firmware . Since the hardware of these DSL modems is basically adapted to either Annex A or Annex B, the performance of such a modem is limited after such a firmware change. Newer Fritz boxes with an international version of the firmware do not have this limitation.
ADSL2 / 2 +
With the ITU G.992.3 / 5 standards with Annex A, B, M and J, the maximum data rates in the receiving and transmitting directions have been increased for ADSL2 / 2 +.
distribution
Germany is the only country in the world that does not use Annex A , i. H. Annex B is also used on analog connections and with ADSL switching without conventional voice telephony ( unbundled DSL , NGN , bitstream access ). For a long time, Deutsche Telekom had only allowed ADSL-over-ISDN connections in its subscriber network , so that even collocation competitors could only implement Annex B; since 2006 there has also been an approval for ITU G.992.5 Annex M, which, however, remained unused until summer 2009.
In the rest of Europe , Russia and the USA , Annex A is predominantly used or in countries with a high ISDN market share (e.g. in Switzerland, Scandinavia, Belgium, the Netherlands and Austria) a mixed operation of Annex A (on analog connections and with pure ADSL / bitstream) and the range and bandwidth-poor Annex B (only on ISDN connections), which Swisscom says is unproblematic.
ADSL and ADLS2 / 2+ standards
| standard | Surname | Receive rate (downstream) | Send rate (upstream) | factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANSI T1.413 Issue 2 | ADSL | 8 Mbit / s | 0.6 Mbit / s | 13.3: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.1 | ADSL (G.dmt) | 8 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 8: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.1 Annex A | ADSL over POTS | 10 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 10: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.1 Annex B | ADSL over ISDN | 10 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 10: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.2 | ADSL Lite (G.lite) | 1.5 Mbit / s | 0.5 Mbit / s | 3: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.3 | ADSL2 (G.bis) | 12 Mbit / s | 1.2 Mbit / s | 10: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.3 Annex A | ADSL2 over POTS | 12 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 12: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.3 Annex B | ADSL2 over ISDN | 12 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 12: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.3 Annex I | All-digital mode ADSL2 | 12 Mbit / s | 3.2 Mbit / s | 3.75: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.3 Annex J. | All-digital mode ADSL2 | 12 Mbit / s | 3.5 Mbit / s | 3.43: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.3 Annex L | RE-ADSL2 | 6 Mbit / s | 1.2 Mbit / s | 5: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.3 Annex M | ADSL2 extended upstream | 12 Mbit / s | 3.5 Mbit / s | 5: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.4 | ADSL2 (G.bis.lite) | 12 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 12: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.5 | ADSL2 + | 24 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 24: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.5 Annex A | ADSL2 + over POTS | 24 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 24: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.5 Annex B | ADSL2 + over ISDN | 24 Mbit / s | 1 Mbit / s | 24: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.5 Annex I | All Digital ADSL2 + | 24 Mbit / s | 3.2 Mbit / s | 7.5: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.5 Annex J. | All Digital ADSL2 + | 24 Mbit / s | 3.5 Mbit / s | 6.86: 1 |
| ITU-T G.992.5 Annex M | ADSL2 + M | 24 Mbit / s | 3.5 Mbit / s | 6.86: 1 |
Individual evidence
- ↑ Swisscom Technology Handbook Spectrum Management (PDF; 276 kB) ( Memento of the original dated December 24, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. P. 5: Mixed operation of ADSL-over-POTS and ADSL-over-ISDN in the same star quad without problems
- ↑ ITU-T Recommendation G.992.1: Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) transceivers
- ↑ ITU-T Recommendation G.992.2: Splitterless asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) transceivers
- ↑ ITU-T Recommendation G.992.3: Asymmetric digital subscriber line transceivers 2 (ADSL2)
- ↑ ITU-T Recommendation G.992.4: Splitterless asymmetric digital subscriber line transceivers 2 (splitterless ADSL2)
- ↑ ITU-T Recommendation G.992.5: Asymmetric Digital SubscriberLine (ADSL) transceivers - Extended bandwidth ADSL2 (ADSL2 +)