Acamptonectes
| Acamptonectes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
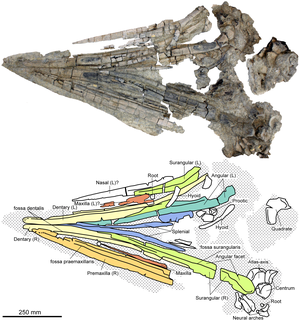
Acamponectes densus holotype skull |
||||||||||||
| Temporal occurrence | ||||||||||||
| Lower Cretaceous ( Hauterivium ) | ||||||||||||
| 133.9 to 130.7 million years | ||||||||||||
| Locations | ||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Acamptonectes | ||||||||||||
| Fischer et al. , 2012 | ||||||||||||
| species | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Acamptonectes is a genus of extinct ichthyosaurs from Lower Cretaceous Europe. The only known species, Acamptonectes densus , was a relatively modern ichthyosaur and lived around 130 million years ago in what is now Europe. Fossil specimens were in the British Speeton and Filey as well as in the German Cremlingen found. Acamptonectes is placed within the ichthyosaurs in the Ophthalmosauridae , the closest relative is Ophthalmosaurus . The fact that ichthyosaurs with Acamptonectes occurred as far as the Lower Cretaceous contradicts an earlier thesis of a mass extinction in this group at the end of the Jurassic .
features
The anatomy of Acamptonectes densus probably largely followed the basic plan of the Thunnosauria . The snout was long, only about 45 mm wide and very low. The lower jaw was covered with relatively small teeth, similar to the closely related Ophthalmosaurus , and ended with a blunt end. The ribs were very strong in comparison with closely related genera, the vertebrae were close together.
Geographical distribution
Acamptonectes has so far been found in southern England ( Speeton Beds ) and in northern Germany ( Cremlingen ). Both regions were covered by part of the Tethys Sea during the Lower Cretaceous .
Stratigraphy and time horizon
The layer of Speeton Beds from which the acamptonectes -Fossilien derived is the basal, the Cremlinger copy the upper Hauterivium allocated. This corresponds to a time frame of 133 to 130 million years. Possibly the genus also extended beyond the Hauterivium into the Albium .
The existence of Acamptonectes during the early Cretaceous relativized the previously popular theory of a mass extinction of ichthyosaurs at the transition from the Jurassic to the Cretaceous period, which only a few representatives would have survived. In fact, not only did the Platypterygiinae with Platypterygius and related taxa persist in the Cretaceous , but also the sister line Ophthalmosaurinae . A short time later, Leninia and Malawania, other Cretaceous ichthyosaurs were described, which testify to the continued existence of various lines.
Systematics and taxonomy
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systematic position of Acamptonectes according to Fischer et al. (2013). The genus is within Ophthalmosaurus , making the latter paraphyletic . |
The type species Acamptonectes densus was identified by Fischer et al. described on the basis of three fossils . A partially preserved skeleton of an adult animal from the Speeton Beds ( GLAHM 132855) served as the holotype ; a find from Filey ( NHMUK R11185) and a fossil of a subadult animal ( SNHM 1284-R) found in 2005 during motorway construction work near Cremlingen served as paratypes . The generic name Acamptonectes is derived from the Greek and means "stiff swimmer" ( ἄκαμπτος for "rigid, stiff" and νήκτης for "swimmer"), the specific epithet densus comes from Latin and means "dense" or "compact". Both names allude to the rigid vertebral column of the species, which had vertebrae closely lined up together. Fischer et al. think one or two other types are possible. However, since the corresponding finds are very fragmentary, they renounced an exact assignment to a taxon and only placed them in or near the genus Acamptonectes .
An osteological analysis of the available fossils revealed a close relationship to the genus Ophthalmosaurus , which existed during the end of the Jurassic. Both lineages diverged in Oxfordian (Late Jurassic). Acamptonectes was thus a relatively modern representative of the Thunnosauria , but more original than Platypterygius .
Sources and References
literature
- Valentin Fischer, Michael W. Maisch, Darren Naish, Ralf Kosma, Jeff Liston, Ulrich Joger , Fritz J. Krüger , Judith Pardo Pérez, Jessica Tainsh, Robert M. Appleby: New Ophthalmosaurid Ichthyosaurs from the European Lower Cretaceous Demonstrate Extensive Ichthyosaur Survival across the Jurassic-Cretaceous Boundary. In: Plos One 7 (1), 2012. doi: 10.1371 / journal.pone.0029234 , e29234. ( Online )
- Valentin Fischer, Robert M. Appleby, Darren Naish, Jeff Liston, James B. Riding, Stephen Brindley, Pascal Godefroit: A basal thunnosaurian from Iraq reveals disparate phylogenetic origins for Cretaceous ichthyosaurs . In: Biology Letters . tape 9 , no. 4 , 2013, p. 1–6 , doi : 10.1098 / rsbl.2013.0021 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Fischer et al. 2012 , pp. 3–5.
- ↑ Fischer et al. 2012 , pp. 5–15.
- ↑ a b Fischer et al. 2012 , pp. 2–3.
- ↑ Fischer et al. 2013 , p. 1.
- ↑ Fischer et al. 2013 , p. 4.
- ↑ Fischer et al. 2012 , p. 2.
- ↑ Fischer et al. 2012 , pp. 16-17.
- ↑ Fischer et al. 2012 , pp. 17-20.