Acetylmethadol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
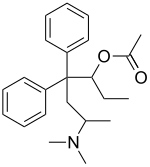
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without specifying the stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Acetylmethadol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 31 NO 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 353,50 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Acetylmethadol ( INN ) (also: Methadyl acetate ( USAN )) is a synthetic opioid - analgesic .
Acetylmethadol should not be confused with alphacetylmethadol (α-acetylmethadol) or levacetylmethadol ( L -α-acetylmethadol). Acetylmethadol is a racemic mixture of alphacetylmethadol and betacetylmethadol, which in turn are racemates of levacetylmethadol (LAAM; L -α-acetylmethadol) and D -α-acetylmethadol or L -β-acetylmethadol and D -β-acetylmethadol. Therefore, acetylmethadol has four possible optical isomers each . All of these isomers have been shown to be able to partially or completely replace the effects of heroin in rats.
Clinical information
application areas
Acetylmethadol is an analgesic with a slow increase in action and a long duration of action. It is mainly used as a substitute drug in the treatment of drug addiction.
Mechanism of action
Acetylmethadol is primarily an agonist of the μ-type opioid receptor . It works similarly to methadone . Acetylmethadol exerts its analgesic effect by binding to the μ-opioid receptor of sensory neurons . Binding to the μ-opioid receptor activates associated G (i) proteins . The subsequent reactions inhibit the formation of adenylate cyclase and thus reduce the level of intracellular cAMP . G (i) activates the potassium channels and inactivates the calcium channels of the cell, causing the neuron to hyperpolarize . The end result is a reduced transmission of the pain impulse in the nerve conduction and a reduced release of neurotransmitters , which reduces the receptors' ability to accept pain signals.
Legal status
Acetylmethadol is listed in Germany in Annex I to the Narcotics Act as a non-marketable narcotic and cannot be prescribed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Heroin discriminative stimulus effects of methadone, LAAM and other isomers of acetylmethadol in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2002, 164 (1): 108-114, PMID 12373424 .
- ^ The Small Molecule Pathway Database .