Achondroplasia
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q77 | Osteochondrodysplasia with growth disorders of the long bones and the spine |
| Q77.4 | Achondroplasia |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
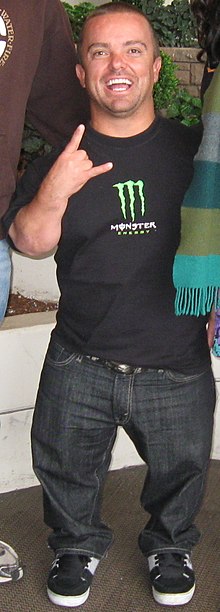
The Achondroplasia is the most common form of genetic dwarfism . Those affected are particularly noticeable for their severely shortened arms and legs and a large head.
designation
In 1878 the term achondrodysplasia was coined by the French doctor Joseph Marie Jules Parrot .
The term achondroplasia (literally: missing cartilage formation) is purely historical and explains neither the cause nor the symptoms of this disorder.
Other terms, which are out of date and no longer in use, are chondrodystrophy , chondrodystrophia fetalis , Parrot syndrome or Kaufmann syndrome (with reference to the German pathologist Eduard Kaufmann ).
frequency
Achondroplasia is the most common form of genetically determined short stature. It occurs with an incidence of 1 in 20,000 births. Like all types of short stature, it is one of the rare diseases .
root cause
Achondroplasia is the result of a point mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor gene FGF R-3 (English: F ibroblast G rowth F actor R eceptor 3 ). This mutation leads to a disruption of cartilage formation ; the bone growth zone ( epiphyseal plate ) is ossified prematurely, which leads to a restriction in length growth, especially of the arms and legs ( extremities ) ( enchondral ossification ). This creates a disproportionate short stature, in which the trunk and head are relatively longer than the extremities.
In 96% of the cases there is a G (1138) A point mutation in the FGFR-3 gene. This leads to an amino acid exchange in position 380 of the protein, glycine becomes arginine (Gly380Arg). In 3% of the cases a G (1138) C point mutation can be detected, which also results in a glycine-to-arginine exchange.
Achondroplasia is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means that it can only be passed on by those who are affected by it. This is the case in approximately 20% of children born with achondroplasia. The remaining 80% have a new mutation of the FGFR3 gene; the short stature arises regardless of the size of the parents. Embryos with a homozygous mutation (both the paternal and maternal variants of the gene are changed) are not viable and die shortly after birth or already in the womb ( thanatophore dysplasia ).
General symptoms of the mutation
Achondroplasia leads to a disproportionate short stature . Since the unusual cartilage formation, especially in the long bones, does not allow regular development, severely shortened extremities with a normal trunk size are characteristic. In contrast, the growth in length is disturbed when the growth in thickness is almost normal.
Other symptoms in affected people are:
- comparatively short fingers
- increased distance between the 3rd and 4th fingers ( trident hand )
- comparatively short neck and large head with a bulging forehead and an unusual skull base
- narrow face with a saddle nose
- often hollow back (hyper lordosis ) or kyphosis
- congenital tightness of the occipital opening and the entire spinal canal ( spinal canal stenosis )
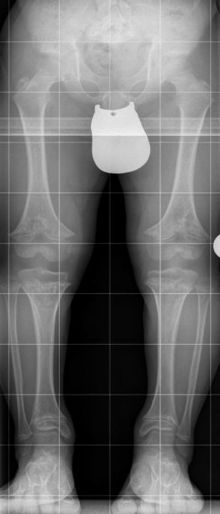
- often bow-legs or knock-knees
- frequent otitis media (due to a narrowed eustachian tube )
- characteristic skin folds (the skin is too wide for the shortened extremities)
Because of their relatively long torso, people affected by achondroplasia have an almost normal seat height. When fully grown, they reach a height of between 120 and 148 cm.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
Clinically, to differentiate it from hypochondroplasia and pseudoachondroplasia , important aspects are the large head ( megalencephaly ) with a balcony forehead and flat nose, prognathy.
Radiological criteria are:
- Broadened metaphyses in normal epiphyses
- Disproportionately shortened humerus and femur
- Narrow sacrum, broad pelvic vane with a horizontal and wide pan roof
- Increasing caudal distance between the arch roots, shortened pedicles with possible spinal stenosis, wedge-shaped deformation of the vertebral bodies
- Trident hand brachydactyly
therapy
The therapy is based on the symptoms. In the case of functional disabilities due to the position of the leg axis and the spine, as well as incipient paralysis, decompressing and stabilizing interventions can be carried out on the spine .
Two compounds are currently in clinical trials for the treatment of achondroplasia. BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. is developing a CNP analog (named Vosoritide) which intervenes in the cascade of action of the FGFR3 receptor and results in an increased rate of division of the cartilage cells. BioClin Therapeutics, Inc. is developing an FGFR3 antibody for both the treatment of bladder cancer and achondroplasia.
See also
literature
- W. Schuster, D. Färber (Ed.): Children's radiology. Imaging diagnostics. Springer, 1996, ISBN 3-540-60224-0 .
- JW Spranger: Bone Dysplasias. Urban & Fischer, 2002, ISBN 3-437-21430-6 .
Single receipts
- ↑ JM Parrot: Les malformations achondrodysplasiques. In: Bulletins de la Société d'anthropologie de Paris, 1878.
- ↑ a b Spranger, Menger, Meinecke, Zabel: Achondroplasie . In: BKMF (Hrsg.): Small stature - yellow leaves . 1a. Bremen March 2007, p. 2 .
- ↑ E. Kaufmann: Studies on the so-called fetal rickets (Chondrodystrophia foetalis). Berlin, Reimer, 1892.
- ↑ Bernhard Zabel: FGFR3 mutations as a cause of skeletal dysplasia in the achondroplasia group. In: Klaus Mohnike ao: Achondroplasia and Hypochondroplasia. 2nd Edition. ABW Wissenschaftsverlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-940615-41-1 , p. 3.
- ↑ F. Hefti: Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer, 1998, ISBN 3-540-61480-X , p. 651.
- ↑ BioMarin Pharmaceutical BMN-111 phase-II results | Biotechnology Events. In: www.biotechnologyevents.com. Archived from the original on April 13, 2016 ; Retrieved April 20, 2016 .
- ↑ BioClin Therapeutics, Inc .: BioClin Therapeutics Initiates Phase 2 Clinical Trial Evaluating B-701 for Treatment of Urothelial Cell Carcinoma. In: www.prnewswire.com. Archived from the original on April 20, 2016 ; Retrieved April 20, 2016 .
- ↑ Science | BioClin Therapeutics. In: www.bioclintherapeutics.com. Archived from the original on May 12, 2016 ; Retrieved April 20, 2016 .
Web links
- Achondroplasia. In: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man . (English)