Active center
As active center (engl. Active site ) is known in the chemistry those sites of a catalyst at which the catalyzed reaction takes place.
properties
The definition can be applied to two classes of catalysis:
Here the active center describes a specific arrangement of atoms on the surface of a solid .
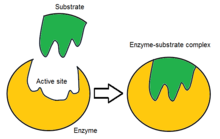
Here the active center describes the area of an enzyme that is responsible for the catalytic effect. In this area, the substrate binds to the enzyme and can be converted there.
The active center of all enzymes that have so far been well investigated is a pocket-shaped or crevice-shaped indentation in the protein molecule. The resulting enlarged contact area enables stronger and more specific binding of the substrate , and in some cases also enantioselectivity . Conversely, the substrate specificity decreases with a smaller contact area. The bond occurs due to ionic bonds , hydrogen bonds , van der Waals interactions , hydrophobic effects and temporary covalent bonds (in the transition state ). The substrate binding creates an enzyme-substrate complex either according to the lock and key principle or according to the induced fit model.
The active center consists of the aforementioned substrate binding region, the catalytic center, e.g. B. with a catalytic triad , and occasionally with a coenzyme . The catalytic center can (to some extent forward and reverse reactions) catalyze only one reaction, thus, it is considered effective specifically referred to. The reaction depends on the cofactors and amino acids present, which participate in the conversion of the substrate.
Competitive inhibitors can also bind to the active center , and because of their shape similar to that of the substrate, they fit into the substrate-binding area.
An occasionally occurring allosteric center and binding sites for other non-competitive or non-competitive enzyme inhibitors do not belong to the active center. An example of an active center is the oxyanion hole in some enzymes.
The molecular modeling attempts to find about computer-aided methods in the representation of the active site new compounds for drug development. An active center can be specifically changed through a protein design . As a result, higher specificity can be achieved or the conversion of other substrates that did not previously fit into the active center.
Individual evidence
- ↑ active center in the Lexicon of Biology , accessed on May 14, 2013.