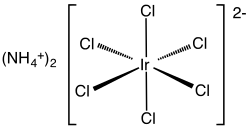
Ammonium hexachloroiridate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Ammonium hexachloroiridate | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | (NH 4 ) 2 [IrCl 6 ] | |||||||||
| Brief description |
black-red to black solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 441.01 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
2.86 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
Decomposition from 200 ° C |
|||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water
|
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Ammonium hexachloroiridate is an inorganic chemical compound from the group of ammonium compounds and hexachloroiridate .
Extraction and presentation
Ammonium hexachloroiridate can be obtained by reacting a solution of disodium hexachloroiridate in aqua regia with ammonium chloride.
properties
Ammonium hexachloroiridate is in the form of black-red to black octahedra, which are sparingly soluble in water. Above 200 ° C it decomposes into iridium , nitrogen , ammonium chloride and hydrogen chloride . It has a sodium hexachloroplatinate (IV) type crystal structure . It can very easily be converted into ammonium hexachloroiridate (III).
use
Ammonium hexachloroiridate is used as an intermediate in the production of pure iridium from ores containing iridium.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d George B. Kauffmann and Larry A. Teter: Ammonium hexachloroiridate (IV) . In: Henry F. Holtzclaw, Jr. (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 8 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1966, pp. 223-227 (English).
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Ammonium hexachloroiridate (IV), 99.99% trace metals basis at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 17, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume II, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 , p. 1736.
- ↑ L: Römpp Lexikon Chemie, 10th edition, 1996-1999 Volume 3: H - L . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-200011-6 , p. 2258 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Josef K. Felixberger: Chemistry for Beginners . Springer-Verlag, 2017, ISBN 978-3-662-52821-1 , pp. 339 ( limited preview in Google Book search).

![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {Na_ {2} [IrCl_ {6}] + 2 \ NH_ {4} Cl \ longrightarrow (NH_ {4}) _ {2} [IrCl_ {6}] \ downarrow + \ 2 \ NaCl} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/33ee66650a7e7639686020a2e6e1cfd736f3ea14)
