Androstanol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
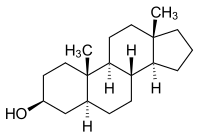
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Androstanol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 32 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 276.46 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
150-152 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Androstanol is a compound from the class of steroidal sex hormones in men, the androgens .
Extraction and presentation
Androstanol was initially obtained from boar testes. It can be synthesized according to the following rule:
Androstan-17 β -ol-3-one (I) is oxidized with chromium (VI) oxide to androstane-3,17-dione (II), which in turn with sodium borohydride to androstan-3-ol-17 β-one ( III) is reduced, which is reacted in a Wolff-Kishner reduction with alkaline hydrazine solution to androstan-3-ol (IV). The synthesis gives a racemate composed of androstane-3 α -ol and androstane-3 β -ol.
Biological importance
Androstanol is a pheromone found in mammals. As an antagonist of the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), androstanol is of importance in the metabolism of foreign substances, so-called xenobiotics , but also of endogenous substances.
literature
- TK Kwan, DJ Trafford, HL Makin, AI Mallet, DB Gower: GC-MS studies of 16-androstenes and other C19 steroids in human semen. In: The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology . 43 (6), 1992, pp. 549-556, doi: 10.1016 / 0960-0760 (92) 90243-C .
- RM Kaminski, H. Marini, PI Ortinski, S. Vicini, MA Rogawski: The pheromone androstenol (5 alpha-androst-16-en-3 alpha-ol) is a neurosteroid positive modulator of GABAA receptors. In: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics . 317 (2), 2006, pp. 694-703, doi: 10.1124 / jpet.105.098319 .
- A. Nixon, AI Mallet, DB Gower: Simultaneous quantification of five odorous steroids (16-androstenes) in the axillary hair of men. In: Journal of Steroid Biochemistry . 29 (5), 1988, pp. 505-510, doi: 10.1016 / 0022-4731 (88) 90185-9 .
- Robic, Faraut, Prunier: Pathways and genes involved in steroid hormone metabolism in male pigs: a review and update. In: The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology . 140, 2014, pp. 44-55, doi: 10.1016 / j.jsbmb.2013.11.001 .
- Melanie Gimpel: GC / C-IRMS in a complex biological matrix: Investigations into the factors influencing the accuracy of the measured isotope ratios using the example of steroid analysis. Dissertation. TU Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-938163-74-0 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Santa Cruz Biotechnology https://www.scbt.com/scbt/de/product/5alpha-androstan-3beta-ol-1224-92-6
- ↑ a b data sheet androstane-3β-diol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 26, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ E. Elisberg, H. Vanderhaeghe, TF Gallagher: Preparation of 3α-Hydroxyetiocholane-17-one by a differential reduction from Sodium boron hydrides. In: J. Am Chem Soc. 74, 1952, pp. 2814-2816. doi: 10.1021 / ja01131a033 .
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links to 5 α -androstane-3 α -ol : CAS number: 7657-50-3, PubChem : 449196 , ChemSpider : 395796 , Wikidata : Q27074463 .
- ↑ George P. Rédei: Encyclopedia of Genetics, Genomics, Proteomics, and Informatics. 3rd edition. Springer, 2008, p. 93.
- ↑ Wen Xie: Nuclear Receptors in Drug Metabolism. John Wiley & Sons, 2008, ISBN 978-0-470-40905-3 , pp. 147 and 170.
- ^ Y. Yamamoto et al .: The role of the nuclear receptor CAR as a coordinate regulator of hepatic gene expression. In: Biophys. 409, 2003, pp. 207-211. PMID 12464260

