Californium (III) bromide
| Crystal structure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
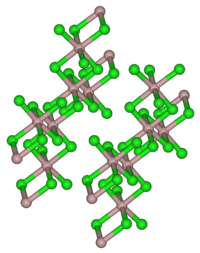
| Crystal lattice of Californium (III) bromide (AlCl 3 type) | |||||||
| Crystal system | |||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Californium (III) bromide | ||||||
| other names |
Californium tribromide |
||||||
| Ratio formula | CfBr 3 | ||||||
| Brief description |
greenish monoclinic crystals |
||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||
|
|||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Molar mass | 490.79 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| Melting point |
675 ° C |
||||||
| Hazard and safety information | |||||||
 Radioactive |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Californium (III) bromide is a bromide of the artificial element and actinide californium with the molecular formula CfBr 3 . Californium occurs in this salt in the +3 oxidation state.
properties
Californium (III) bromide is a green solid. With increasing temperatures it partially decomposes to Californium (II) bromide (CfBr 2 ):
Californium bromide crystallizes (III) both in the AlCl 3 - and in the FeCl 3 -type . In the first case, the Cf ion is six-coordinate and the three independent Cf – Br bond lengths are 279.5 ± 0.9 pm, 282.7 ± 1.1 pm and 282.8 ± 0.8 pm.
Although the proportion of divalent Californium increases with increasing temperature, only the monoclinic structure (AlCl 3 type) could be detected for CfBr 3 .
With the radioactive decay of the Berkelium isotope 249 Bk to 249 Cf, the oxidation number and the respective crystal structure are preserved. The six-coordinate BkBr 3 (AlCl 3 type, monoclinic structure) produces a six-coordinate CfBr 3 ; the eight-coordinate BkBr 3 ( PuBr 3 type , orthorhombic structure) produces an eight-coordinate CfBr 3 , a previously unknown form of CfBr 3 .
The enthalpy of solution of californium (III) bromide in 1 M hydrochloric acid (at 298.15 ± 0.05 K and p 0 = 101,325 kPa) was measured to be - (181.4 ± 0.9) kJ mol −1 . Together with the results of the enthalpy of solution of Californium metal , the standard enthalpy of formation (Δ f H 0 ) could be determined to be - (752.5 ± 3.2) kJ mol −1 .
safety instructions
Classifications according to the CLP regulation are not available because they only include chemical hazard and play a completely subordinate role compared to the hazards based on radioactivity . The latter also only applies if the amount of substance involved is relevant.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Californium (III) bromide at www.webelements.com.
- ↑ The hazards emanating from radioactivity do not belong to the properties to be classified according to the GHS labeling. With regard to other hazards, this substance has either not yet been classified or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Californium bromide (CfBr 3 ): The crystal shows green color .
- ↑ John H. Burns, JR Peterson, JN Stevenson: Crystallographic Studies of Some Transuranic Trihalides: 239 PuCl 3 , 244 CmBr 3 , 249 BkBr 3 and 249 CfBr 3 , in: J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. , 1975 , 37 (3), pp. 743-749 ( doi: 10.1016 / 0022-1902 (75) 80532-X ).
- ↑ JP Young, KL Vander Sluis, GK Werner, JR Peterson, M. Noé: High Temperature Spectroscopic and X-Ray Diffraction Studies of Californium Tribromide: Proof of Thermal Reduction to Californium (II) , in: J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. , 1975 , 37 (12), pp. 2497-2501 ( doi: 10.1016 / 0022-1902 (75) 80878-5 ).
- ↑ JP Young, RG Haire, JR Peterson, DD Ensor, RL Fellows: Chemical Consequences of Radioactive Decay. 1. Study of 249 Cf Ingrowth into Crystalline 249 BkBr 3 : A New Crystalline Phase of CfBr 3 , in: Inorg. Chem. , 1980 , 19 (8), pp. 2209-2212 ( doi: 10.1021 / ic50210a003 ).
- ↑ J. Fuger, RG Haire, WR Wilmarth, JR Peterson: Molar Enthalpy of Formation of Californium Tribromide , in: Journal of the Less Common Metals , 1990 , 158 (11), pp. 99-104 ( doi: 10.1016 / 0022- 5088 (90) 90435-M ).
literature
- Richard G. Haire: Californium , in: Lester R. Morss, Norman M. Edelstein, Jean Fuger (Eds.): The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements , Springer, Dordrecht 2006; ISBN 1-4020-3555-1 , pp. 1499-1576 ( doi: 10.1007 / 1-4020-3598-5_11 ).
![{\ displaystyle {\ ce {2 CfBr3 -> [\ Delta T] 2 CfBr2 + Br2}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/062d1518dc82fcbfc0ee0fe5d9e89f34653c012d)