Carbometalation
The carbometalation is a representation method for Elementorganyle d. H. chemical compounds from metals and classical organic groups. When the reaction is a nucleophilic - addition reaction in which takes place the driving force from the bond formation.
The starting materials represent a metal organyl MR and an organic compound with a CC multiple bond . The product obtained is the corresponding insertion product in which the metal atom is linked to the former organyl part via the multiple bond of the organic substance. The metal must be sufficiently electropositive for the reaction or the starting material is a transition metal alkyl with an electron deficiency situation. The metal organyl compounds of the elements lithium to cesium and aluminum are therefore very suitable.
The carbometalation insertion reaction is stereoselective with respect to reaction with alkynes . The reaction proceeds in the sense of a cis addition to the triple bond. The reverse reaction of the carbometalation is known as β-decay and represents an elimination reaction . The mechanism of the carbometalation proceeds as a concerted course of the reaction, i. H. the conversion steps during the reaction take place simultaneously and not in chronological order from one another.
Examples
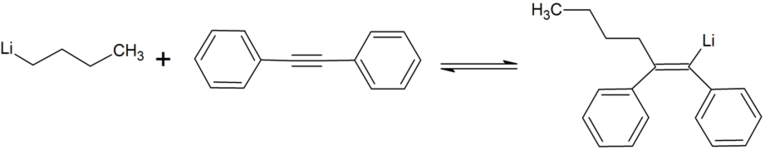
An example reaction is the reaction of n-butyllithium with an alkyne-bridged diphenyl to give the corresponding cis-addition product .
Industrial application
Carbometalation is used on an industrial scale in the polymerization of butadienes to synthetic rubber - when using isoprene as the starting material - with the use of organyl lithium.
Other industrial processes in which carbometalation is used is the Ziegler build-up reaction, in which ethene is not selectively oligomerized. The reactions are typically based on aluminum organyls.
swell
- C. Elschenbroich : Organometallchemie , Teubner Verlag, 5th edition, 2005
- RH Crabtree: The Organometallic Chemistry of the Transition Metals , Wiley & Sons, 4th Edition 2005
- AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 .