Insertion reaction
An insertion reaction is a type of reaction in organic chemistry . Here a bond is formally broken in the substrate used , a molecule fragment is inserted and the broken bond is re-established at the other end of the fragment. Insertion reactions are often found in metal- catalyzed reactions. These include the insertion of carbon monoxide as a carbonyl group , the insertion of alkenes or alkynes and the CH insertion .
Polymerization
Insertion reactions occur during polymerizations . The Ziegler-Natta process for the synthesis of polyethylene is an example of this. Mechanistically, it follows the Cossee-Arlman mechanism . The existing bond of the titanium complex to the first carbon atom of the polymer chain is broken and a molecule of ethylene is inserted. The bond now runs from the catalyst via the inserted fragment to the previous end of the chain, as a result of which chain growth around a C 2 unit was achieved.
CO insertion
Many insertions of carbon monoxide in the context of metal-catalyzed reactions with the formation of carbonal compounds are described in the literature. For this purpose, the reaction is usually carried out under high CO pressures.
Hydroformylation
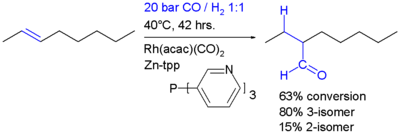
The hydroformylation , also called oxo process, is used for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. The classic catalyst is a four- coordinate cobalt complex, which is formed from dicobalt octacarbonyl . After addition of the complex to the alkene, carbon monoxide is inserted into the Co-C bond, whereby the carbonyl group of the later aldehyde is built up.
However, this insertion is not only reserved for cobalt complexes. Other metal complexes for hydroformylation have also been developed. One of the best known is the rhodium- catalyzed hydroformylation.
Palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions
Many palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions can be used for the insertion of carbon monoxide. This includes, for example, the Heck reaction .
Other reactions
In the cycle of the Pauson-Khand reaction to build cyclopentenones, both an alkene and carbon monoxide are inserted into existing cobalt-carbon bonds. The same happens in the Dötz reaction , in which an alkyne and then carbon monoxide are inserted.
CH insertion
Insertions in carbon- hydrogen bonds are rarely found, but are of synthetic interest. Examples are the alkylations by rhodium carbenoid complexes by CH insertion. The rhodium cabenoid formed for this purpose, which is accessible from diazo compounds , cleaves the CH bond. This reaction also enables the construction of otherwise difficult to access four-membered ring systems, such as cyclobutane and propiolactone derivatives.
swell
- ^ B. Tieke, Makromolekulare Chemie , 2nd edition, Wiley-VCH, 2005, ISBN 978-3527313792 .
- ^ A b Hans Beyer and Wolfgang Walter : Textbook of Organic Chemistry , 23rd edition, S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1998, ISBN 3-7776-0808-4 , p. 409.
- ^ F. Calderazzo: Synthetic and Mechanistic Aspects of Inorganic Insertion Reactions. Insertion of carbon monoxide , in: Angew. Chem. 1977 , 89 , 305-317. doi : 10.1002 / anie.19770890506
- ^ DE Cane, PJ Thomas: Synthesis of (dl) -pentalenolactones E and F , in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984 , 106 , 5295. doi : 10.1021 / ja00330a044
- ↑ E. Lee, KW Jung, YS Kim: Selectivity in the lactone formation via C --- H insertion reaction of diazomalonates , in: Tetrahedron Lett. 1990 , 31 , 1023-1026. doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (00) 94420-4