Pauson-Khand reaction
The Pauson-Khand reaction (short: PK reaction or PKR; also: cyclopentenone annulation ) is a chemical name reaction as well as a multi-component reaction for the synthesis of substituted cyclopentenones , which was mainly developed by the British-Jewish chemist Peter Ludwig Pauson (1925-2013) and by the Indian chemist Ihsan U. Khand (1935-1980) and Graham R. Knox and William E. Watts in 1971 at the University of Strathclyde in Glasgow . It is a [2 + 2 + 1] cycloaddition , for which an alkene , an alkyne and carbon monoxide and dicobalt octacarbonyl are required.
mechanism
The reaction mechanism of the Pauson-Khand reaction is not fully established. The following mechanism is postulated as the most likely: First, two CO ligands are removed from the cobalt octacarbonyl, for example oxidatively . The subsequent addition of an alkyne produces a dicobalta tetrahedran (see also Nicholas reaction ). After another CO ligand has dissociated, the alkene is added, after which CO is again complexed on the metal . The later carbonyl function is introduced by nucleophilic attack on a carbonyl carbon . The reaction ends with the ring closure to the five-membered ring and the cleavage of dicobalt hexacarbonyl.
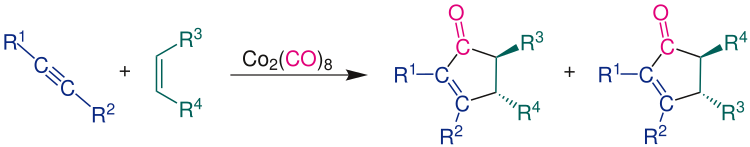
Products
The Pauson-Khand reaction produces a mixture of two racemic regioisomers. Only one enantiomer of the two regioisomers is shown here:
Intramolecular reaction
In addition to the intermolecular variant already presented, there is also an intramolecular variant of the Pauson-Khand reaction. The drawn asterisks * mark centers of chirality.
Variations
Instead of the classical cobalt catalyst also other transition metal catalysts, for example the can Wilkinson catalyst on rhodium can be used. Other catalyst systems with molybdenum , iron or iridium have also been used successfully.
literature
Primary literature
- Ihsan U. Khand, Graham R. Knox, Peter L. Pauson, William E. Watts: A cobalt induced cleavage reaction and a new series of arenecobalt carbonyl complexes . In: Journal of the Chemical Society D . Chemical Communications . No. 1 , 1971, p. 36 , doi : 10.1039 / C2971000036A .
- Ihsan U. Khand, Graham R. Knox, Peter L. Pauson, William E. Watts: Organocobalt complexes . Part I. Arene complexes derived from dodecacarbonyl tetracobalt. In: Journal of the Chemical Society . Perkin Transactions 1 . No. 0 , 1973, p. 975-977 , doi : 10.1039 / P19730000975 .
- Ihsan U. Khand, Graham R. Knox, Peter L. Pauson, William E. Watts, Michael I. Foreman: Organocobalt complexes . Part II. Reaction of acetylenehexacarbonyldicobalt complexes, (R 1 C 2 R 2 ) Co 2 (CO) 6 , with norbornene and its derivatives. In: Journal of the Chemical Society . Perkin Transactions 1. No. 0 , 1973, p. 977-981 , doi : 10.1039 / P19730000977 .
- Ihsan U. Khand, Peter L. Pauson: Organocobalt complexes . Part VIII. Specificity of the cyclopentenone synthesis from acetylenehexacarbonyldicobalt complexes and norbornene derivatives. In: Journal of the Chemical Society . Perkin Transactions 1. No. 1 , 1976, p. 30-32 , doi : 10.1039 / P19760000030 .
- Peter L. Pauson, Ihsan U. Khand: Uses of Cobalt-Carbonyl Acetylene Complexes in Organic Synthesis . In: Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences . tape 295 , 1977, pp. 2-14 , doi : 10.1111 / j.1749-6632.1977.tb41819.x .
Secondary literature
- Philip D. Magnus, Lawrence M. Principe: Origins of 1,2- and 1,3-stereoselectivity in dicobaltoctacarbonyl alkene-alkyne cyclizations for the synthesis of substituted bicyclo [3.3.0] octenones . In: Tetrahedron Letters . tape 26 , no. 40 , 1985, pp. 4851-4854 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (00) 94968-2 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Helmut Werner : Peter Ludwig Pauson (1925–2013) . In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition . tape 53 , no. 10 , 2014, doi : 10.1002 / anie.201400432 .
- ^ William J. Kerr: The Pauson-Khand Reaction. Scope, Variations and Applications . Ed .: Ramon Rios Torres. John Wiley & Sons , New York 2012, ISBN 978-0-470-97076-8 , The Pauson-Khand Reaction - an Introduction, pp. 3–4 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Ihsan U. Khand, Graham R. Knox, Peter L. Pauson, William E. Watts: A cobalt induced cleavage reaction and a new series of arenecobalt carbonyl complexes . In: Journal of the Chemical Society D . Chemical Communications. No. 1 , 1971, p. 36 , doi : 10.1039 / C2971000036A .
- ↑ Eberhard Breitmaier, Günther Jung: Organic chemistry. Basics, substance classes, reactions, concepts, molecular structure . 5th edition. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 3-13-541505-8 , p. 95 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Christian Maaß, Torben Böhnisch: Pauson-Khand and other co-mediated reactions. (PDF) (No longer available online.) Georg-August-Universität Göttingen , December 9, 2007, formerly in the original ; Retrieved March 3, 2014 . ( Page no longer available , search in web archives )