China alligator
| China alligator | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

China alligator ( Alligator sinensis ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Alligator sinensis | ||||||||||||
| Fauvel , 1879 |
The Chinese alligator ( Alligator sinensis ) is a species of crocodile and, besides the Mississippi alligator, which is widespread in North America, is the only recent species of the subfamily of real alligators (Alligatorinae).
description
Alligator sinensis can reach a maximum length of 220 cm, but mostly only 150 to 180 cm. The males are significantly larger and longer than the females. The carapace is predominantly yellowish-gray in color and has dark bands on the back and tail. The limbs are quite short and strong, the feet each have five claws. Under water, the powerful tail serves as a rudder.
distribution
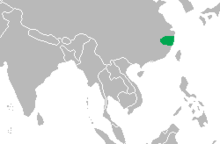
The Chinese alligator is endemic to the mouth of the Yangtze River and its tributaries on the Chinese Pacific coast of the Anhui - and parts of the neighboring Zhejiang and Jiangsu provinces . The historical area of distribution encompassed other areas of China and reached as far as Korea , in the years from 1978 to 1998 the area of distribution was reduced by more than 90 percent. As the discovery of a 3 million year old fossil of a Chinese alligator shows, the lizards also lived in Japan at the end of the Pliocene .
Way of life
The Chinese alligator lives in still waters such as swamps, ponds and lakes as well as in slowly flowing rivers. He stays almost exclusively in the water. Like most crocodiles, it is a food generalist and primarily hunts fish, waterfowl, small mammals and crustaceans, and young animals also eat insects and snails.
Systematics
The Chinese alligator ( Alligator sinensis ) is a species of crocodile and, besides the Mississippi alligator, which is widespread in North America, is the only type of real alligator (Alligatorinae).
| Crocodiles (crocodylia) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Hazard and protection
The population of the Chinese alligator is threatened with extinction because it has been hunted intensively for years for its leather, meat and as a souvenir and is still sometimes illegally hunted. It is also threatened due to the destruction of potential habitats. It has been classified as endangered in the IUCN Red List since 1982 and is currently classified as critically endangered. It is also listed in Appendix I of the CITES lists and is therefore excluded from trading. 120 specimens still live in the wild worldwide. In China, attempts are being made to breed offspring in “breeding centers”. In December 2008, 40 scientifically managed zoological gardens around the world were holding 111 Chinese alligators, including twelve in seven zoos in Europe. There is a European Conservation Breeding Program (EEP) of the European Zoo Association EAZA. The stud book has been maintained by Dr. Norbert Fritsch, Neunkirchen Zoological Garden .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Masaya Iijima, Keiichi Takahashi, Yoshitsugu Kobayashi: The oldest record of Alligator sinensis from the Late Pliocene of Western Japan, and its biogeographic implication. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, Volume 124, 1 July 2016, Pages 94–101, doi: 10.1016 / j.jseaes.2016.04.017
- ↑ Herbert Reinke-Nobbe: Spiders in bottles . In: Focus . No. 25 , June 16, 2008, p. 50 .
- ↑ EAZA - EEPs . In: archive.is . May 16, 2016 ( archive.today [accessed July 3, 2018]).
swell
- Behler, J. (1993): Species Survival Plan for the Chinese alligator . Crocodile Specialist Group Newsletter 12 (4): 18.
- Chen, B. (1990): Preliminary studies of the home range of the Chinese alligator . In: Crocodiles . Proceedings of the 10th Working Meeting of the Crocodile Specialist Group. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. pp. 43-46.
- Jinzhong, F. (1994): Conservation, management and farming of crocodiles in China . In: Crocodiles . Proceedings of the 2nd Regional Meeting of the Crocodile Specialist Group. IUCN & Conservation Commission of the Northern Territory, Australia.
Web links
- Alligator sinensis in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2006. Posted by: Crocodile Specialist Group, 1996. Retrieved on 11 May, 2006.
- Alligator sinensis in The Reptile Database
- China alligator on the Animal Diversity Web
- China Alligator Datasheet from the World Zoo Association WAZA