Chlorous acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
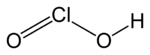
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Chlorous acid | ||||||||||||
| other names |
Chloro (III) acid |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | HClO 2 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
only stable in aqueous solution |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 67.44 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| pK s value |
1.97 |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
The chlorous acid is one of the oxygen-containing acids of chlorine. Since it decomposes rapidly in water, chlorine dioxide and hydrochloric acid even in a dilute cold solution , it is of little importance in its free form.
The salts of chlorous acid are the chlorites . Compared to free acid, they are more stable and can be isolated in pure form, but they are reactive substances and effective oxidizing agents , which must be taken into account when handling.
Manufacturing
Chlorous acid is obtained by reacting barium chlorite and sulfuric acid . Barium sulfate precipitates as a by-product .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
Web links
Commons : Chlorous acid - Collection of pictures, videos, and audio files

