Code sun
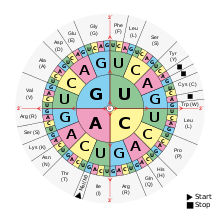
The so-called code sun is a schematic representation of the genetic code and is used to translate the base triplets of the mRNA into the corresponding canonical amino acid .
In the protein biosynthesis , there are two main processes: in the transcription of the sequence of is nucleotides of a portion on the DNA rewritten in the nucleotide sequence of a RNA and on this basis the so-called mRNA produced. In eukaryotic cells this process takes place in their nucleus , in prokaryotic cells like bacteria in the cytosol of the cell. In both cases, the process of translation then takes place in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes , which translates the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA into the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain formed in the process . A sequence of three bases , a triplet , corresponds to the codon for a certain of the proteinogenic amino acids or a stop codon .
The code sun is read from the inside out. For example, the base sequence 5'-GCA-3 'on the mRNA leads to the incorporation of the amino acid alanine (Ala).
The code sun was introduced in the textbook Classical and Molecular Genetics by Carsten Bresch and Rudolf Hausmann , published in 1972, and today, in addition to the tabular form, it is a common way of representing the amino acid coding using the base triplets of the mRNA.
literature
- Carsten Bresch , Rudolf Hausmann : Classical and Molecular Genetics . Third, expanded edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York 1972, ISBN 3-540-05802-8 .
Web links
- Pohlmeyer, Roland: Genetic Code from a Different Perspective. Codon sun rearranged . Lab journal online; Retrieved June 20, 2009
Individual evidence
- ^ Carsten Bresch , Rudolf Hausmann : Classical and molecular genetics . Third, expanded edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York 1972, ISBN 3-540-05802-8 .