Cold Seep
Cold seeps , cold vents , cold springs or cold seepage points are sources in the sea where "cold" water (not heated) emerges from the subsoil. In contrast, at the hydrothermal springs also observed on the seabed, including the black smokers , spring water of up to 400 ° C can be measured.
Description of the main types
Groundwater sources
In the vicinity of a coast, fresh water under the surface of the water can leak from a spring into the sea. Such headwaters are found, for example, in the Mississippi Delta and the Niger Delta.
Methane sources
Almost two million cubic kilometers of water are suspected in the sediment of the sea floor and in the oceanic crust below , which, for example, can flow out of the subsurface , triggered by tectonic movements of the sea floor in a subduction zone . This occurs partly in the area of the accretion wedge , a wedge-shaped accumulation of pushed sediments to form a smaller sub-sea mountain range. The pore water is pressed out of the originally very water-containing sediments . In addition, a diagenetic conversion of loose sediment to sedimentary rock and the dissolution of gas hydrates can trigger cold seas. There are also cold springs on continental slopes , with the seawater coming from deeper sediment layers.
Substances such as methane and hydrogen sulfide are dissolved in this spring water , which is why an ecosystem tailored to this environment can arise even at the bottom of the lightless deep sea . Here, for example, beard worms and mussels can be found that live in symbiosis with bacteria . These microorganisms can use chemosynthesis to obtain their energy from the substances that are dissolved in the water of the cold seeps. Such communities can take the energy necessary for survival, comparable to the biocenoses of black smokers , directly from the earth's interior and are therefore independent of solar energy.
The cold spring area is characterized by the fact that calcium carbonate is deposited in crusts up to the calcite and aragonite compensation depth and that gas hydrates can be found.
Saline solution
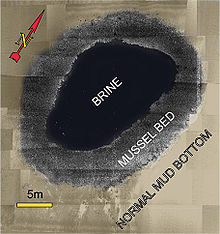
As a result of rising fossil salt horizons ( salt dome ), a salt solution ( brine ) can spring up from the sea floor ( brine seep ). Since water with a high salt content is heavier than normal sea water, this brine can run into depressions on the sea floor and form salt ponds (English: brine pools ) there. In the Gulf of Mexico , there are several such salt ponds. Their chemism has not yet been finally explored. At the edge of some salt ponds, mussels live together with methane-loving bacteria if the brine is enriched with methane.
Gas and oil storage facilities
Sometimes cold seas can arise as a by-product of natural gas or oil production . That is why they are called Oil-Field Brines in English .
Individual evidence
- ↑ J. Greinert, W. Weinrebe, P. Gimpel, J. Brockhoff2: (...) investigation of cold fluid vent sites and associated gas hydrate occurrences
- ^ Bob Carney: Lakes Within Oceans