Dune tiger beetle
| Dune tiger beetle | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Dune tiger beetle ( Cicindela hybrida ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Cicindela hybrida | ||||||||||||
| Linnaeus , 1758 |
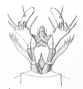
| Images of the larva according to Reitter and Lampert | |||

|
x210px |

|

|
| Head from below | Lower jaw | ||

|
|||
| in the residential tube | At sight | antenna | bottom lip |
The dune tiger beetle or copper brown tiger beetle ( Cicindela hybrida ) is a ground beetle from the subfamily of the tiger beetles (Cicindelinae).
features
The beetles are 11 to 16 millimeters long and have a relatively variable body color. They are usually greenish-copper in color, but there are also copper-brown or bluish specimens. The underside is metallic green, the upper lip is light. The pronotum is colored in rainbow colors in many species. The wings have white or yellow serrated bands (spots). The basal spot has roughly the shape of a C. The forehead (front) is hairless, and there are no bristles below the compound eyes . The missing hair distinguishes the species from the similar mountain tiger beetle ( C. sylvicola ), whose forehead is hairy. The first antenna segment has only a few white bristles at the tip.
Occurrence
The animals are found in Europe as far as northern Finland , central Sweden and southern Norway . To the east, the distribution area extends across Asia Minor and the Caucasus to Siberia . They inhabit sandy areas, such as B. dunes in sand pits , sandy, open forests, river banks, sandy meadows and fields and dirt roads from the lowlands to higher altitudes. You can find them from April to October.
Way of life
The adults and larvae feed on insects . The adults can perceive larger prey (e.g. soft beetles ) from a distance of 20 to 30 centimeters, small prey (e.g. ants) from approx. 10 centimeters with their very good eyesight. The larvae live in tubes up to 50 centimeters long, the entrance of which faces south. The larvae often build their tubes close together.
literature
- Ekkehard Wachmann , Ralph Platen, Dieter Barndt: Ground beetles - observation, way of life. Naturbuch Verlag, Augsburg 1995, ISBN 3-89440-125-7
- Jiři Zahradnik, Irmgard Jung, Dieter Jung et al .: Beetles of Central and Northwestern Europe. Parey, Berlin 1985, ISBN 3-490-27118-1 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Edmund Reitter : Fauna Germanica, the beetles of the German Empire. Volume I, KGLutz 'Verlag, Stuttgart 1908.
- ↑ Kurt Lampert: Pictures from the life of the beetle. Series A Volume 2 Strecker & Schröder, Stuttgart 1909.
Web links
- www.naturbildarchiv-guenter.de Picture story on the biology and networking of the dune tiger beetle Cicindela hybrida