Dichlormid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
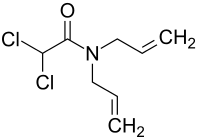
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dichlormid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 11 Cl 2 NO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
|
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 208.09 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
5.0–6.5 ° C (technical) |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
130 ° C (1.3 mPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (5 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dichlormid is a herbicidal safener developed by Stauffer Chemical and introduced in 1972 . Today it is distributed by AstraZeneca .
Extraction and presentation
Dichlormid can be obtained by reacting dichloroacetyl chloride and diallylamine .
use
Dichlormid increases the tolerance of thiocarbamate and chloroacetamide herbicides to cultivated crops by increasing glutathione-S-transferase activity. This accelerates the breakdown of the herbicide into glutathione conjugates. Other researchers have found that dichlormid reverses the inhibition of lipid biosynthesis by EPTC .
It is used in combination with the herbicide for weed control, especially in maize.
Admission
Since acetochlor is not approved in the EU, dichlormid is not used here either.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on Dichlormid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 21, 2014.
- ↑ a b Datasheet Dichlormid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 21, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Aqel W Abu-Qare, Harry J Duncan: Herbicide safeners: uses, limitations, metabolism, and mechanisms of action . In: Chemosphere . tape 48 , no. 9 , September 2002, p. 965-974 , doi : 10.1016 / S0045-6535 (02) 00185-6 ( iranarticles.com [PDF]).
- ↑ AstraZeneca and its genetic research - Feeding the world or fueling hunger? P. 18.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 17 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
