The (semiconductor technology)
A The ([ daɪ ], English for "dice", "flakes", dt i plural A. "This"; English plural.:. Dice or the [ daɪs ] and the [ daɪ ]) is in the semiconductor and micro-systems technology the name of an individual, unpackaged piece of semiconductor - wafer . Such a die is usually obtained by sawing or breaking the finished wafer into rectangular parts ( dicing ). Usually there is a component on a die, e.g. B. a transistor, light emitting diode, or a complex assembly, e.g. B. Integrated circuit , a microsystem . In order to benefit from parallel production on the wafer for as long as possible, the dicing takes place last in the normal production process, directly before installation in a housing or attachment to a circuit carrier (see direct assembly ). These are then called " chips " or " naked chips ". Even if a wafer (planned) is divided (even unstructured) before the component or assembly is completed, the sections are referred to as dies.
etymology
The term “ die ” comes from kitchen English: “ slice and dice ” means - for example a cucumber - “first cut into slices and then dice”. Accordingly, one begins with the production of integrated circuits with a - cucumber-like - silicon bar , this is then "cut into slices" - from this the " wafer " = "waffles" - and then "chopped up" - from this then the " dice " = "Cube". Since the wafers are very thin, the “ dice ” do not look cube-shaped, but rather correspond to very flat cuboids in their shape.
"Bare Chip"
" Bare chip " or " bare die " (German "Nacktchip") are integrated electronic components that are not conventionally built into a plastic or ceramic housing, but are processed without a housing. They are applied directly to a circuit board or a ceramic substrate and electrically connected to surrounding components by means of wire bonding .
application
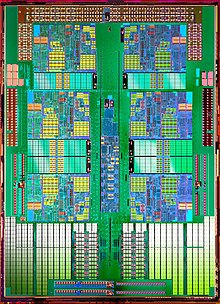
As integration progresses, more and more assemblies that were previously attached as individual chips next to each other on a circuit board are combined on a common chip. Meanwhile, several hundred million transistors for CPUs , GPUs or RAM are housed on a die with an area of around one square centimeter .
| product | The dimensions | Die area (mm²) | Technology node | Number of transistors (million) | Comment / component |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel 4004 | 3 mm × 4 mm | 12 | 10 µm PMOS | 0.0023 | Main processor, first microprocessor |
| Intel Itanium 2 (Tukwila) | 21.5 mm × 32.5 mm | 698.75 | 65 nm bulk CMOS | 221 | Multi-core main processor |
| AMD Phenom II X6 | 346 | 45 nm | 750 | Multi-core main processor | |
| Nvidia Fermi GF110 | 520 | 40 nm | 3000 | Graphics processor | |
| AMD Cayman (RV970) | 389 | 40 nm | 2640 | Graphics processor | |
| Intel Core i7-980X | 248 | 32 nm | 1170 | Multi-core main processor | |
| AMD FX | 315 | 32 nm | 1200 | Multi-core main processor | |
| Nvidia Kepler GK110 B | 533 | 28 nm | 7100 | Graphics processor | |
| AMD Tahiti (R1000) | 365 | 28 nm | 4310 | Graphics processor | |
| Nvidia Pascal GP100 | 610 | 16 nm FinFET | 15300 | Graphics processor | |
| NVIDIA Volta GV100 chip | 815 | 12 nm FinFET | 21100 | Graphics processor |
Digital and analog signal circuits can increasingly be accommodated on a chip with power electronic elements (e.g. BiCMOS technology).
A combination of two complementary assemblies, such as CPU and cache , on the same chip can be described with the term “ on- die ”: The CPU has the cache “ on- die ”, which enables higher clock rates and bus widths and thus the exchange of data significantly accelerated.
processing
The assembly and connection technology (AVT, packaging ) deals with the further processing of the dies - housing and integration into the circuitry environment .
A known good die (KGD) is a semiconductor chip that has been tested according to the specifications and found to be good, which, depending on the product , can contain a single component, for example a transistor , or a complex circuit such as a microprocessor . Good or defective data can also be determined in the wafer assembly using electrical needle testers. Defective components used to be identified by a colored dot ( inked ) and are excluded from the subsequent process of contacting and housing (cycle II, packaging ).
The ratio of useful to the total number of all available on a wafer as this will yield (engl. Yield ) and is an important indicator for evaluating the manufacturing process and the efficiency of a production line.
literature
- Graham Neil: Time is right for bare die. In: European Semiconductor , 27, No. 11, 2005, pp. 11-12.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ According to Google: "semiconductor dice" - 6 hits; "Semiconductor Thies" - 339 hits; Status: 03/2018
- ↑ Yvonne Attiyate, Raymond Shah: Dictionary of microelectronics and microcomputer technology with explanations / Dictionary of Microelectronics and Micro Computer Technology with definition. Springer, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-13444-3 , p. 42 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Guy De la Bédoyère: The First Computers. Evans Brothers, 2005, ISBN 0-237-52741-3 , p. 36 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Lambert Saddle Elicke, Eric DeLano: Intel Itanium quad-core Architecture for the Enterprise. (PDF) 2010, p. 5 , accessed on July 12, 2015 (presentation slides, Eighth Workshop on Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing Architectures and Compiler Technology (EPIC-8)).
- ↑ a b c nVidia GK104: 3.54 billion transistors on a chip area of just 294mm². 3DCenter.org, March 13, 2012, accessed June 21, 2014 .
- ↑ heise online: GTC 2016: Nvidia unveils Pascal monster chip with 16 GByte HBM2 and up to 3840 cores. In: heise online. Retrieved August 23, 2016 .
- ↑ heise online: GTC 2017: Nvidia introduces giant GPU Volta with 5120 cores and 16 GByte HBM2. In: heise online. Retrieved October 15, 2018 .

