Pyrrolines
The pyrrolines or dihydropyrroles are a group of substances in organic chemistry. They include three heterocyclic compounds and their derivatives . The three basic structures of this group, which differ in the position of their double bond , are the cyclic imine 1-pyrroline , the cyclic enamine 2-pyrroline and the cyclic amine 3-pyrroline . Their basic structure is derived from pyrrole , from which they formally arise through the hydrogenation of a double bond.
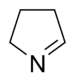
|
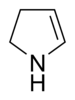
|

|
| 1-pyrroline | 2-pyrroline | 3-pyrroline |
Pyrrolines represent a structural element of the more complexly structured porphyrins . These consist of two alternating pairs of pyrrole and pyrroline, which are bridged by methine groups .
Occurrence
1-pyrroline was found as an oxidation product of putrescine in many plants such as peach fruits, wheat , corn and spinach leaves and as a component of the poisonous secretion of the fire ant species Solenopsis punctaticeps .
Individual evidence
- ^ AW Galston, TA Smith: Polyamines in Plants. Springer, 1985, ISBN 978-90-247-3245-6 .
- ^ GG Habermehl: Poison animals and their weapons. Springer, 1987, ISBN 978-3-540-56897-1 .
