Diisopropylbenzenes
| Diisopropylbenzenes | ||||||
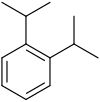
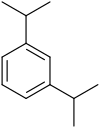
| Surname | 1,2-diisopropylbenzene | 1,3-diisopropylbenzene | 1,4-diisopropylbenzene | |||
| other names | o -diisopropylbenzene | m -diisopropylbenzene | p -diisopropylbenzene | |||
| Structural formula |
|
|

|
|||
| CAS number | 577-55-9 | 99-62-7 | 100-18-5 | |||
| PubChem | 11345 | 7450 | 7486 | |||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 18 | |||||
| Molar mass | 162.28 g mol −1 | |||||
| Physical state | liquid | |||||
| Melting point | −57 ° C | −63 ° C | −17 ° C | |||
| boiling point | 205 ° C | 203 ° C | 210 ° C | |||
| solubility | very sparingly soluble in water | 0.072 mg l −1 in water (25 ° C) | practically insoluble in water | |||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
|||
| H and P phrases | see above | no H-phrases | no H-phrases | |||
| see above | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | ||||
| see above | no P-phrases | no P-phrases | ||||
In chemistry , the diisopropylbenzenes form a group of substances whose structure consists of a benzene ring with two isopropyl groups (–CH (CH 3 ) 2 ) as substituents . Their different arrangement results in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 12 H 18 .
properties
The boiling points of the diisopropylbenzenes are almost the same. The melting points differ more clearly. The 1,4-diisopropylbenzene, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point.
Web links
Commons : Diisopropylbenzenes - Collection of pictures, videos, and audio files
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 1,2-diisopropylbenzene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 7, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 1,3-diisopropylbenzene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 7, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 1,4-diisopropylbenzene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 7, 2018(JavaScript required) .