Epimer
In chemistry , epimers are special stereoisomers with at least two stereocenters which differ in configuration at only one stereocenter , with the exception of the last asymmetric one. All other stereocenters in the molecules, if any, are the same. The anomer is a special case of the epimer in which the configuration at the anomeric carbon atom changes ( mutarotation ).
In the nomenclature , the prefix “epi-” is added to one of the epimeric pairs , for example for quinine and epi- quinine . If the pairs are enantiomers , the prefix “ent-” is used.
Examples
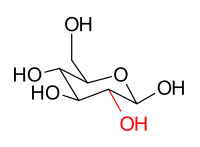
The sugars glucose and mannose are epimers. For example, β- D - glucopyranose and β- D - mannopyranose differ because they only have a different stereochemical configuration at the C-2 position. The hydroxy group of β- D -glucopyranose is in the equatorial position (in the “plane” of the ring), while the C-2 hydroxy group of β- D -annopyranose is in the axial position (out of the “plane” of the ring). However, since the images are not mirrored, these are not enantiomers, but epimers:
 |

|
| β- D -glucopyranose [contains five stereocenters, including one anomeric center (right)] |
β- D -mannopyranose |
Likewise, D - erythrose and D - threose are epimers. Also cis -Dekalon and trans -Dekalon are epimers, the latter is more stable:
 |

|
|
cis -decalone (contains two stereocenters) |
trans -decalone |
Doxorubicin and Epirubicin are two closely related drugs and epimers:

|
| Comparison of doxorubicin and epirubicin |
Other such compounds are epi- inositol and inositol :
 |

|
|
epi -inositol (contains six stereocenters) |
Inositol (contains six stereocenters) |
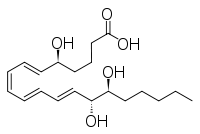
Other epimers are lipoxin and epi- lipoxin:
 |

|
| Lipoxin | epi lipoxin |
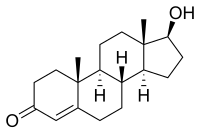
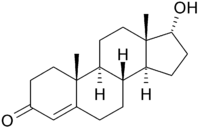
Testosterone and 17- epi -testosterone are also epimers:
 |
|
| Testosterone (contains six stereocenters) |
17- epi -testosterone (contains six stereocenters) |
Epimerization
Epimerization is a chemical process in which an epimer is converted into its chiral counterpart. An example of this would be the condensed tannins - depolymerization . Epimerization can be spontaneous (generally a slow process) or catalyzed by enzymes . The latter happens during the epimerization between the sugar N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmannosamine , which is catalyzed by RENBP , a renin- binding protein.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Joachim Buddrus, Bernd Schmidt: Fundamentals of organic chemistry. 5th edition, de Gruyter Verlag, Berlin 2015, ISBN 978-3-11-030559-3 , pp. 760–761.