Doxorubicin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
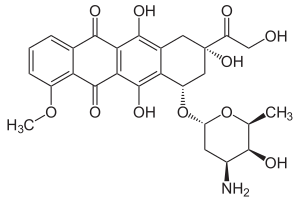
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Doxorubicin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
205 ° C (decomposition) (doxorubicin hydrochloride) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
8.2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Easily soluble in water, methanol, acetonitrile and tetrahydrofuran (doxorubicin hydrochloride) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Doxorubicin is the hydroxy derivative of daunorubicin and belongs to the group of anthracyclines . The compound is a stereoisomer of epirubicin and is used as a stereochemically pure drug in chemotherapy ( cytostatic ). Doxorubicin belongs to the group of active substances called intercalants . The effect is based on the intercalation in the DNA .
properties
Doxorubicin acts as an intercalant on planar connections in DNA and RNA. DNA synthesis is disrupted, topoisomerase II is inhibited and radical formation occurs.
Doxorubicin has fluorescence properties that can be used to study the discharge of doxorubicin from the cell. A involviertes in such processes protein is the first of a doxorubicin-resistant lung cancer - cell line cloned MRP1 of the family of ABC transporters . Doxorubicin can also be used to clarify the localization of the proteins involved in Multiple Drug Resistance and the role of organelles such as the Golgi apparatus and lysosomes .
Applications
Doxorubicin is used as a cytostatic agent in the treatment of tumors such. B. mammary carcinomas , bronchial carcinomas and lymphomas . The drug is administered intravenously in these indications . For the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in particular, it is used intraarterially as part of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). It is applied either in an emulsion with an oily contrast medium (Lipiodol) or bound to drug-releasing particles.
Side effects
The most significant side effects include bone marrow depression , nephrotoxicity , cardiotoxicity (cumulative dose-dependent dilated cardiomyopathy ), ulceration and dermatotoxic effects. An accumulation in tumor-independent tissue such as the heart can take place; this is counteracted by means of PEGylation in order to concentrate the levels in the plasma and tumor tissue.
The most effective method of preventing doxorubicin-induced dilated cardiomyopathy ("adriamycin cardiopathy"), which can occur months after administration, is the administration of dexrazoxane .
Trade names
Monopreparations doxorubicin: Adriblastin (D, A, CH), Adrimedac (D), Ribodoxo (D), various generics (D, A, CH)
Monopreparation liposomal-encapsulated doxorubicin: Myocet (D, A)
Monopreparation PEG-liposomal-encapsulated doxorubicin: Caelyx (D, A, CH)
literature
- M. Ghione, J. Fetzer, H. Maier (Ed.): Results of Adriamycin Therapy . Adriamycin Symposium, Frankfurt am Main 1974. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York 1975.
- J. Fetzer, D. Füllenbach, H. Gabel (Eds.): Adriamycin. Solid tumors, hemoblastoses; new ways of chemotherapy . Volume 1-3. Kehrer, Freiburg i. Br. 1977-1980.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ A b The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 14th edition. Merck & Co., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006, ISBN 0-911910-00-X , p. 582.
- ↑ Entry on doxorubicin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 25, 2019.
- ↑ a b c data sheet Doxorubicin hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 28, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on doxorubicin in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ S. Ayla, I. Seckin et al.: Doxorubicin induced nephrotoxicity: protective effect of nicotinamide. In: International journal of cell biology. Volume 2011, p. 390238. doi: 10.1155 / 2011/390238 . PMID 21789041 . PMC 3140777 (free full text).
- ^ B. Kunkel, M. Kaltenbach, Paul Schölmerich : Diseases of the endocardium, myocardium and pericardium, cardiac tumors and cardiac trauma. In: Rudolf Gross , Paul Schölmerich, Wolfgang Gerok (Eds.): 1000 memoranda of internal medicine. Schattauer, Stuttgart / New York 1971; 4th, completely revised edition, ibid. 1989 (= UTB für Wissenschaft / Uni-Taschenbücher. Volume 522), ISBN 3-7945-1282-0 , pp. 90–96, here: p. 93.
- ↑ Rote Liste Service GmbH (Ed.): Rote Liste 2017 - drug directory for Germany (including EU approvals and certain medical devices) , Rote Liste Service GmbH, Frankfurt / Main, 2017, edition 57, ISBN 978-3-946057-10 -9 , p. 1286.