Fusicoccin A
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
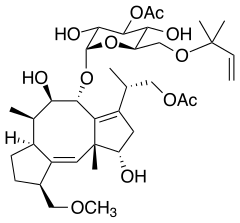
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fusicoccin A | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 36 H 56 O 12 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 680.82 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Fusicoccin A (often referred to simply as fusicoccin ) is a terpenoid that is synthesized as a toxin by the parasitic Deuteromycetes Fusicoccum amygdali . Infested plants, mostly peach and almond trees , die from the effect of the toxin, which leads to the irreversible opening of the stomata ( stomata ) and thus to drying out ( wilting ). The molecular basis for this is the activation of the plasma membrane H + -ATPase in the guard cells caused by fusicoccin . This leads to the opening of voltage-controlled channel proteins and the influx of potassium cations into the guard cells. The subsequent osmotic influx of water into the guard cells leads to their swelling, so that the stomata open and more water escapes.
Fusicoccin A is used in plant physiology to research the phytohormone auxin and the regulation of stomal movements. In biochemistry , fusicoccin A is used in the chemically induced dimerization of certain fusion proteins .
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Johansson, F. et al. (1993): Fusicoccin Activates the Plasma Membrane H + -ATPase by a Mechanism Involving the C-Terminal Inhibitory Domain . In: Plant Cell. 5 (3); 321-327; PMID 12271065 ; PDF (free full text access).