GTO thyristor
The GTO thyristor ( English gate turn-off thyristor ) is a thyristor that can be switched on like a normal thyristor with a positive current pulse at the control input - the gate . In contrast to the normal thyristor, it can also be switched off by means of a negative current pulse (which is up to a third of the load current).

Differences to the normal thyristor
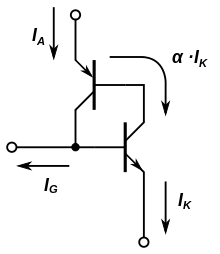
As can be seen from the equivalent circuit diagram , there is no difference in the basic structure to a conventional thyristor. The difference lies in the manufacturing process, i.e. the geometric arrangement of the components on the silicon. The parallel connection of many individual thyristors can be seen in the sectional view .
technology
In principle, it would also be possible to switch off a normal thyristor with a negative current pulse at the gate. However, this would only begin to “localize” due to the negative gate current, which means that the silicon area in which a current flow is possible is reduced. The remaining live area would be overloaded and self-destruct.
A GTO thyristor is generally divided into such small, individual thyristors connected in parallel that each individual thyristor no longer has the opportunity to localize, but has to switch off. With the parallel connection, however, there is the difficulty of switching off all of them at the same time, since otherwise the same destructive effect occurs as with conventional thyristors.
properties
The switch-on time of the GTO thyristors is even improved by the parallel connection compared to the normal thyristor. It is therefore also used where fast switch-on times are required, e.g. B. in radar systems. However, with the advent of FETs , it has been almost completely replaced in these areas. The greatest disadvantage of GTO thyristors is the complex wiring of the gate connection. In addition to the fact that the current at the gate can flow in both directions and is also very large in the negative direction (the switch-off current gain is very small, so that the switch-off current must be up to a third of the load current), the current must be limited to avoid destruction.
The thyristors, which can be relatively small for high currents, need a whole capacitor bank, depending on the application, to provide the high currents for switching off. The volume requirement of these capacitors is a multiple of the actual GTO thyristor.
Due to the long clearing times for the shutdown, the switching frequency is also limited to approx. 1 kHz.
| Forward voltage | before ignition 50 V to 5 kV | |
| after ignition 0.6 V to 3 V | ||
| Forward current | up to 3 kA | |
| Reverse voltage | up to 5 kV |
Purposes
GTO thyristors are used in power converters for various purposes, especially in power electronics and traction technology for electric vehicles. Today, however, they are increasingly being replaced by IGBTs and are only used at very high powers.
Further developments
- IGC thyristor ( Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor )
- MTO thyristor
- MC thyristor ( MOS Controlled Thyristor )
literature
- Thomas Tille, Doris Schmitt-Landsiedel : Microelectronics. Semiconductor components and their use in electronic circuits . Springer Verlag, 2004, ISBN 978-3-540-20422-0 .
Web links
- Semiconductor components in power electronics . Lecture notes for power electronics and converter technology I at the University of Bremen