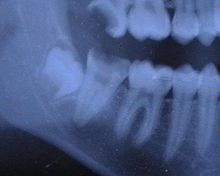
Germectomy
A germectomy (from the Latin germinare "germinate" and Greek : έκτέμνειν (ektémnein) "cut out") is the removal of a tooth germ . A germectomy is performed almost exclusively on the wisdom teeth .
indication
A germectomy is performed almost exclusively for orthodontic reasons, because the number and size of the teeth often do not correlate with the size of the jaw, which means that the teeth can become crowded and nestled.
The best time to have a germectomy is when the tooth crown is formed but the tooth roots are not yet mineralized. At this stage, the tooth germ lies loosely in the tooth follicle (tooth sac) and is not yet anchored in the bone.
Surgical technique
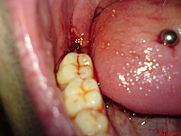
After appropriate anesthesia , an incision is made and a periosteal mucosal flap is formed. Sometimes the tooth germ can already be recognized because the jaw bone has already been broken through by the tooth germ, but usually a bone window still has to be milled through which the tooth germ and tooth follicle can then be lifted out. If the bone window is to be kept small, the tooth germ can also be dismantled and removed in pieces. It is important that the tooth sac is also completely removed. Failure to do this can result in the formation of a follicular cyst. Finally, any sharp bone edges are removed and the wound is sutured. Wound healing complications rarely occur after a germectomy because the procedure is not as serious and the tooth germ, tooth sac and tooth socket are sterile because they have not yet had any connection to the oral cavity. For this reason, several tooth germs are often removed in one session.
Tooth transplantation
A removed tooth germ can also be inserted into a tooth gap or in place of a tooth that has already been deeply destroyed. This option is primarily used in the lower jaw of the six-year-old molar . This can be done immediately after the tooth removal or later. At the implantation site , a “suitable” cavity (hollow space) is prepared in the bone, into which the tooth germ and tooth follicle are then inserted. In the case of a tooth transplant , it is particularly important that the operation is carried out extremely gently so that the tooth follicle is not damaged and the root growth can continue and complete. In addition, care must be taken to ensure that the (existing) alveoli are no longer infected if the tooth is transplanted immediately after the extraction . B. after apical periodontitis or cyst formation may be the case.
Tooth germ removal is an autoplasty (autologous transplantation), which is the transplantation of the body's own tissue.
swell
- ↑ Der kleine Stowasser : Latin-German school dictionary
- ↑ GEMOLL : Greek-German school and manual dictionary
See also
- Tooth root
- dentition
- Assessment standard for dental services, BEMA no. 64 (Germ)
- Tooth scheme
- Tooth formula