Heptaphs
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
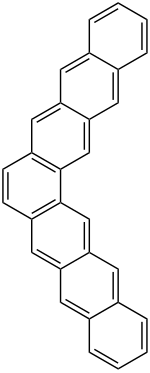
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Heptaphs | |||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 30 H 18 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
pale orange solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 378.46 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
473-474 ° C |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Heptaphene is a chemical compound from the group of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons .
Extraction and presentation
Heptaphene can be obtained by reducing heptaphendichinone with acetic acid and zinc in pyridine .
properties
Heptaphene is a pale orange solid that fluoresces green in solution. It dissolves in sulfuric acid to form a purple-red solution.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Eric Clar: Polycyclic Hydrocarbons . Springer Science & Business Media, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-01665-7 , pp. 418 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.