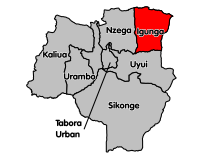
Igunga (district)
| Igunga district | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Basic data | |
| Country | Tanzania |
| region | Tabora |
| surface | 6912 km² |
| Residents | 399,727 (2012) |
| density | 58 inhabitants per km² |
| ISO 3166-2 | TZ-24 |
Coordinates: 4 ° 23 ' S , 33 ° 28' E
Igunga is a district of the Tabora region in Tanzania , its administrative center is in the city of Igunga . The district borders the Shinyanga region in the north, the Singida region in the east, the Uyui district in the south and the Nzega district in the west .
geography
Igunga has an area of 6,912 square kilometers and around four hundred thousand inhabitants (2012 census). The district lies on the central high plateau of Tanzania at an altitude of 1000 to 1200 meters above sea level. The drainage takes place to the east into the outflowless Lake Kitangiri . Many of the rivers and streams are temporary, the largest river is the Manonga, which also forms the northern border. The climate in Igunga is a local steppe climate, BSh according to the effective climate classification . The rainfall is low, mostly less than 1000 millimeters per year. This makes the country one of the driest areas in Tanzania. It rains most in the months of December to April, the dry season from June to September is almost without rain. The annual average temperature is 23.5 degrees Celsius.
history
In 1975 Igunga was separated from the Nzega district and has been an independent district ever since.
Administrative division
The district consists of the four divisions Igunga, Simbo, Manonga and Igurubi and a total of 35 parishes (as of 2019):
| division | Area km 2 |
Number of municipalities |
|---|---|---|
| Igunga | 2484 | 9 |
| Igurubi | 1410 | 7th |
| Manonga | 1439 | 11 |
| Simbo | 1579 | 8th |
| total | 6912 | 35 |
populationThe population increased from 203,367 in 1988 to 324,094 in 2002 and further to 399,727 in 2012. This means that the annual growth decreased from 3.3 to 2.1 percent. Almost half of the over-five year olds spoke Swahili, five percent spoke Swahili and English, and almost half were illiterate (as of 2012). Facilities and services |
 |
- Education: 137 primary schools and 33 secondary schools are available for the education of young people (as of 2019).
- Health: There are two hospitals, five health centers and 59 pharmacies in the district. Of the hospitals, one is state-run and the second in Nkinga is a private hospital.
Economy and Infrastructure
|
 |
politics
In Igunga, a District Council is elected every 5 years. In the 2019 election, Peter Onesmo Maloda became chairman.
Others
- Climate change: From 2016 to 2019, the European Union funded the “Integrated Approaches to Adaptation to Climate Change” project in Igungu with 1.6 million euros. The goals of the individual projects were to improve ecological sustainability and increase food security.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d History | Igunga District Council. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ^ A b Tanzania Regional Profiles, 14 Tabora Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, p. 16 , accessed on April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ Maps for the World, Map 500k - xb36-2. Russian Army Maps, accessed April 16, 2020 (Russian).
- ↑ Igunga climate: Average Temperature, weather by month, Igunga weather averages - Climate-Data.org. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ^ Well Wishes in Tanzania's Driest District. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ^ Tanzania Regional Profiles, 14 Tabora Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, p. 75 , accessed on April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ Takwimu (Statistics). Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ Health | Igunga District Council. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ Kilimo | Igunga District Council. Retrieved April 16, 2020 (Swahili).
- ^ Tanzania Regional Profiles, 14 Tabora Regional Profiles. (PDF) The United Republic of Tanzania, 2016, pp. 169, 172 , accessed on April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ Machimbo ya dhahabu. Retrieved April 16, 2020 (Swahili).
- ^ Tanzania Trunk Road Network. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ Igunga District Council | Home. Retrieved April 16, 2020 .
- ^ Eco-Village Project Launched at Igunga. allAfrica, March 25, 2016, accessed April 16, 2020 .
- ↑ HANDING-OVER EVENT OF THE EU FUNDED ECO-VILLAGE PROJECT IN IGUNGA, TABORA. Retrieved April 16, 2020 (Norwegian Bokmål).