Impeller
An impeller is a propeller enclosed in an annular or tubular housing . The construction principle is similar to that of ducted propellers used in aircraft . Applications outside the aerospace sector are described here.
properties
By lowering the air resistance induced on the propeller blades, the casing increases the propeller efficiency compared to a non-cased propeller. The reason for the increase in efficiency is to reduce the tip vortex losses that occur at propeller, blade and wing tips. A higher proportion of the energy supplied to a ship's propeller, a fenestron or a fan is converted into kinetic energy of the fluid than without a casing. The same applies to the energy transferred from the fluid to the propeller, which is also greater when the propeller is sheathed. Examples of this are speedometers or jacketed wind turbines. The latter would be more effective than conventional wind turbines, but are not implemented for reasons of structural complexity. Impellers are also used where the risk of damage from free-running propellers is to be reduced.
Applications
Ship propulsion
In the jet propulsion of a watercraft also an impeller operates. In a jet ski , the internal impeller reduces the risk of injuring swimmers and also makes it possible to slide the vehicle onto a beach instead of landing on a jetty, since no propeller can be damaged. Jacketed rotors working in the air flow are known as ducted propellers and are used in swamp boats , ground-effect vehicles and for propulsion and propulsion of hovercraft .
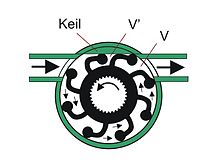
Impeller pump
Impellers are also used in pumps , usually with flexible blades. The fact that these impellers are also referred to as impellers is misleading, however, because they are not predominantly axially acting constructions of the Helix type , but so-called vane wheels (also known as “positive displacement pumps ”). The diameter of the impeller is larger than the inner diameter of the pump housing, which means that the blades made of elastic, rubber-like material are bent. A narrowing in the pump housing between inlet and outlet, the so-called wedge or ridge, causes the blades to bend more in this area. As a result, the volume V 'in the area of the wedge is significantly smaller than the volume V at the suction opening, so that the medium follows the rotary movement of the vane wheel in the area of the pump housing that is opposite the wedge. This leads to the promotion in the direction of rotation.
Impeller pumps are used in particular to cool boat engines . Seawater is sucked in and pumped through the engine with single-circuit cooling and through a heat exchanger with dual-circuit cooling. The cooling water then exits again, usually through the exhaust. A lack of water shows that the cooling water circuit is interrupted and there is a risk of engine damage due to overheating.
A particular advantage of impeller pumps is that they are self-priming. Due to the good sealing effect of the elastic blades on the pump housing, impeller pumps can also suck in air. This creates a vacuum at the suction opening, which sucks in the water actually to be pumped.
Impeller pumps, however, are very susceptible to a prolonged absence of the liquid medium to be conveyed. If, for example, the intake opening of an impeller pump of a boat engine is closed because an object has blocked the opening or the seawater valve has not been opened, the impeller will run dry. After a while, the flexible blades tear off, depending on the quality of the impeller pump, between a few seconds and several minutes. In addition, the individual fragments of the blades are distributed in the cooling water circuit and clog it. When changing the impeller, make sure that all blades are bent against the direction of rotation of the impeller.
Another disadvantage is the strong friction of the impeller in the housing, which devours a considerable part of the drive power, which is therefore not available for the actual media delivery.
These pumps are also often used when conveying food (beverages), the suction capacity reduces hygienically disadvantageous openings in the system, and the media are also spared, as the "whirling effect" is less than with centrifugal pumps (milk).
Power plants
In hydropower plants , water turbines with impellers are sometimes used to convert the flow of liquid into the rotary motion to drive the generator ; Furthermore, some steam turbines also use impellers if water vapor previously heated by other energy sources serves as an energy carrier.
Model aircraft
In model aircraft , rapidly rotating, now mostly electrically powered, impellers are used to obtain the typical appearance of a jet engine that would be disturbed by a propeller. The noise development is also more similar to a jet drive due to the high speed of up to approx. 50,000 / min.
Speed measurement
A log is used to measure the travel through water (relative speed) of a watercraft . In one embodiment of the log, an impeller is arranged in a tube which is oriented open on both sides in the direction of travel. The rotary movement of the impeller is scanned optically or electromechanically with a generator and fed to a display unit.
metallurgy
In light metal smelting companies, impellers made of graphite or ceramic have been increasingly used for melt treatment since 1980 , be it to remove impurities or to bring additions of melt treatment agents into intensive contact with the melt. As a rule, the salt mixtures that clean the melts and remove unwanted impurities are mostly in granulated, low-dust form. Useful alloying elements can also be introduced into the melt using an impeller.
The practice is not limited to the mere impeller effect, but rather introduces a reactive or inert gas mixture, such as chlorine / argon or nitrogen / argon, at the same time and in the dosage coordinated with the gas flow by means of a corresponding additional device. This results in both an increased cleaning effect, i.e. the reduction of disruptive elements such as hydrogen and / or oxides , as well as an optimized distribution and thus more sustainable reaction of useful elements introduced into the melt, predominantly those of a type influencing the structure.
The rotation of the melt caused by the impeller also prevents segregation .
See also
Web links
- [1] ZUWA-Zumpe GmbH in Laufen, Bavaria