John N. Shive
John Northrup Shive (born February 22, 1913 in Baltimore , † June 1, 1984 ) was an American physicist and inventor .
He grew up in New Jersey , received his BS in physics and chemistry from Rutgers University in 1934 and his Ph.D. in 1939. at Johns Hopkins University with a thesis on the modulation of Geiger counters (Practice and theory of the modulation of Geiger counters). From 1939 he was at Bell Laboratories .
At Bell Laboratories he researched semiconductors and in 1948 experimented with tip transistors . During experiments with gold electrodes on both sides of a thin germanium layer (thickness 0.01 cm) he discovered that defect electrons diffuse through the material (and not just on the surface). He announced this internally at Bell Labs on February 18, 1948. This was an essential confirmation of the practicality of a transistor made of two pn junctions (junction transistor), an idea that of William Bradford Shockleyat Bell Labs had recently been developed, but which he kept to himself until the discovery of Shive prompted him to uncover it. Soon after Shive, Shockley and J. Richard Haynes showed that they were indeed positive minority charge carriers in n-type germanium. Side by side with this article, Shive's article appeared in Physical Review.
In 1948 he invented the phototransistor , it was only made known on March 30, 1950 by Bell Laboratories. At that time they were still in development and were used by Bell Laboratories in 1953 in punch card readers in telephone exchanges.
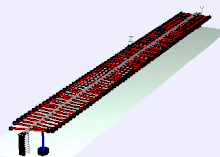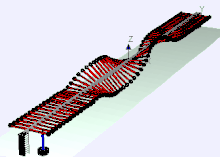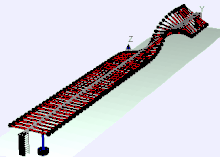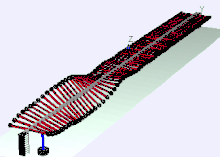
Later he was Director of Education and Training at Bell Labs, where he invented a wave machine that later found its way into many physics collections from demonstration experiments and science museums. Bell Labs published a film about it in 1959 and later a booklet.
He was a Fellow of the American Physical Society and the American Association for the Advancement of Science .
Fonts
- The Properties, Physics and Design of Semiconductor Devices. Van Nostrand, Princeton, NJ 1959.
- Similarities of Wave Behavior. 1961 (created for Bell Telephone Laboratories for training purposes).
- Physics of Solid State Electronics. CE Merrill, Columbus, Ohio 1966.
- with Robert L. Weber: Similarities in Physics. Wiley, 1982, ISBN 0-85274-540-0 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Shockley himself said this in 1976 in The path to the conception of the junction transistor . In: IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices . tape 23 , no. 7 July 1976, p. 597-620 , doi : 10.1109 / T-ED.1976.18463 .
- ^ JR Haynes, W. Shockley: Investigation of Hole Injection in Transistor Action . In: Physical Review . tape 75 , no. 4 , February 15, 1949, p. 691-691 , doi : 10.1103 / PhysRev.75.691 .
- ^ John N. Shive: The Double-Surface Transistor . In: Physical Review . tape 75 , no. 4 , February 15, 1949, p. 689-690 , doi : 10.1103 / PhysRev.75.689 .
- ↑ The story is also presented in Michael Riordan, Lillian Hoddeson, Conyers Herring: The invention of the transistor. In: Rev. Mod. Phys. Volume 71, Issue 2 (Centenary Edition), 1999, S336 – S345, especially S341 f., Doi: 10.1103 / RevModPhys.71.S336
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Shive, John N. |
| ALTERNATIVE NAMES | Shive, John Northrup (full name) |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | American physicist and inventor |
| DATE OF BIRTH | February 22, 1913 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Baltimore |
| DATE OF DEATH | June 1, 1984 |