Jonathan Sisson
Jonathan Sisson (* around 1690 in Lincolnshire ; † 1749) was an English optician and designer and manufacturer of astronomical and geodetic measuring instruments . He is considered the inventor of the modern theodolite .
Sisson began as an apprentice to the London clockmaker and academician George Graham (1673-1751) and started his own business in London in 1722. But he continued to cooperate with Graham and later with the instrument maker John Bird , especially for navigation instruments . It soon became known for the precision of its partial circles and altazimuths .
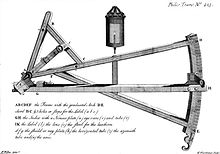
In 1725 he was the first to build a theodolite that had a telescope instead of a sight on the alidade . He improved the circular division of astronomical wall quadrants and also made a contribution to the further development of portable quadrants , u. a. of the Davis Quadrant .
His products were known throughout Europe for their high precision; He received one of his major orders for the La Specola University Observatory in Bologna, founded in 1727 . With John Bird he built the large 8-foot quadrant of the wall for Greenwich and that of the Paris observatory for Le Monnier .
His son, the young Sisson Jeremiah Sisson (1736–1788) took over the London company after his father . The navigation gyro (rotating mirror) he invented served as an artificial horizon on ships .
Web links
literature
- Instruments by Jonathan & Jeremiah Sisson
- Joseph Johann von Littrow : The miracles of heaven or common understanding of the world system, Astr. Instruments, p. 671
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Sisson, Jonathan |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | English optician and measuring instrument maker |
| DATE OF BIRTH | around 1690 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Lincolnshire |
| DATE OF DEATH | 1749 |