Potassium azide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
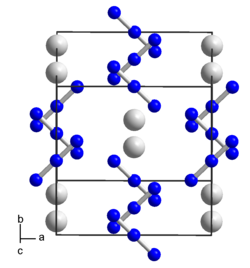
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Rb + __ N 1 / 3− | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
tetragonal |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
I 4 / mcm (No. 140) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 6.1129 Å, c = 7.0943 Å |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium azide | |||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | CN 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 81.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.038 g · cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
355 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Potassium is the potassium salt of hydrogen azide and belongs to the group of azides .
Extraction and presentation
Potassium can be obtained by reaction of hydrogen azide and potassium hydroxide are obtained.
It can also be obtained by reacting potassium carbonate with hydrazoic acid.
Description and characteristics
Potassium azide is a very toxic chemical that also reacts explosively when exposed to ultraviolet light or when heated to a great extent. It disproportionates to metallic potassium and nitrogen gas . Potassium azide is not sensitive to impact like heavy metal azides. The reaction equation works as follows:
It crystallizes in a tetragonal crystal structure with the space group I 4 / mcm (space group no. 140) and Z = 4. with the lattice constants a = 6.1129 Å and c = 7.0943 Å.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Roger Blachnik (Ed.): Pocket book for chemists and physicists . Volume III: Elements, Inorganic Compounds and Materials, Minerals . founded by Jean d'Ans, Ellen Lax. 4th, revised and revised edition. Springer, Berlin 1998, ISBN 3-540-60035-3 , pp. 510 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b c data sheet Potassium azide, ≥99.9% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 18, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 458.
- ↑ EPA TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory : Section 8 (b), Potassium azide ; 1998.
- ↑ Inorganic Syntheses . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 0-470-13264-7 , pp. 79 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Pradyot Patnaik: A Comprehensive Guide to the Hazardous Properties of Chemical Substances . John Wiley & Sons, 2007, ISBN 978-0-471-71458-3 , pp. 615 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b C. C. Addison: Inorganic Chemistry of the Main-Group Elements . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1974, ISBN 0-85186-762-6 , pp. 54 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Ulrich Müller: Refinement of the crystal structures of KN 3 , RbN 3 , CsN 3 and TlN 3 . In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry . tape 392 , no. 2 , 1972, p. 159-166 , doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19723920207 .



