Climatic wind tunnel
A climatic wind tunnel (also called thermal wind tunnel ) is used to determine, optimize and further develop the thermal properties of vehicles and vehicle components.
According to Hucho, the area of application is divided into three groups depending on the air jet cross-section :
The environmental conditions are displayed in a climatic wind tunnel. These are defined by the influencing variables air temperature , air humidity and solar radiation . The air pressure , as the last parameter, is usually not adjustable. But there are special test stands ( altitude chambers ) that make this possible, but at the expense of other parameters. Also, the check-in and flow around is the vehicle by the wind to simulate, for it is several times for the heat balance significantly: The Fahrzeugumströmung causes or affects the flow through the engine compartment, the passenger compartment and all arranged in the cooling air flow heat exchanger . It is responsible for the heat transfer on the vehicle surfaces . In contrast to aerodynamic or aeroacoustic wind tunnels , climatic wind tunnels usually have a single-axis or all-wheel roller test bench . This allows the vehicle to be operated under road-like loads .
The equipment of such ducts - air temperature control, air humidity control , roller test bench , solar radiation - enables investigations to be carried out under the conditions of the most varied of climatic zones , as are necessary in the course of vehicle development .
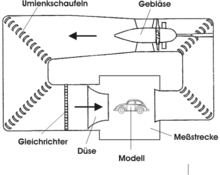
Air duct
For a climatic wind tunnel, only the "Göttingen construction", the closed circuit, can be considered as the air duct . For reasons of space and / or costs, the ducts are usually built "upright". The fan is located above the measuring section - also known as the plenum - and conveys the air to the heat exchanger via a diffuser . There it is brought to the desired temperature . The tempered air is humidified and reaches the antechamber via deflection corners, is accelerated in the nozzle , enters the measuring section with the desired wind speed , flows around the vehicle and is caught by the "collector". The air is returned to the fan via further deflection corners, thus closing the cycle.
The individual components of the air duct
jet
The nozzle size significantly influences the quality of the air flow around the vehicle. For reasons of economy , however, one is forced to limit the nozzle size. If both passenger cars and commercial vehicles are to be examined in a climatic wind tunnel, the nozzle size must be variable (due to the different sizes of the end faces ). Here you can find different designs :
- Nozzles that are only drawn in horizontally in the first part . In the second part, the cross-section is changed vertically with parallel side walls
- Nozzles which are constructed three-dimensionally in the first section (permanently installed) as well as in the second section .
For thermal tests with cars , a beam cross-section of AN = 6 m² has proven to be sufficient (source: Hucho)