Long-nosed dogfish
| Long-nosed dogfish | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
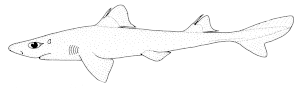
Long-nosed dogfish ( Squalus blainville ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Squalus blainville | ||||||||||||
| ( Risso , 1827) |
The long-nosed dogfish ( Squalus blainville ) belongs to the order of the dogfish-like (Squaliformes).
Appearance
Long-nosed dogfish are a maximum of one meter long. They are gray or brown in color, the underside is light. There are thorns in front of the two dorsal fins. Like almost all species of the Squalea , they lack the anal fin.
The small teeth of the upper and lower jaw overlap. Its tip curves backwards horizontally, the edges are sawn.
distribution
The long-nosed dogfish lives in the eastern Atlantic , from the Bay of Biscay to Namibia , in the Mediterranean , and in the eastern Pacific near Taiwan and Japan . There have also been reports of occurrences in the western Atlantic, as well as in the Indian Ocean and the South Pacific. However, it is not certain whether this has been confused with other dogfish. Long-nosed dogfish prefer to stay above the continental slopes at depths of 15 to 700 meters.
Way of life
The sharks are active, slow swimmers. They live individually or in larger flocks, sometimes separated by sex. Bone fish , smaller cartilaginous fish, crustaceans , cephalopods and bristle worms are eaten by the animals. Long-nosed dogfish are viviparous. They get up to 2 to 4 youngsters per litter.
literature
- Alessandro de Maddalena, Harald Bänsch: Sharks in the Mediterranean , Franckh-Kosmos Verlags-GmbH, Stuttgart 2005 ( ISBN 3-440-10458-3 )
Web links
- Long-nosed dogfish on Fishbase.org (English)
- Squalus blainville inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Threatened Species . Posted by: Ebert, DA, Serena, F. & Mancusi, C., 2008. Retrieved December 5, 2013.
