Leonurine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
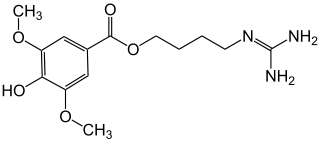
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Leonurine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 21 N 3 O 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 311.33 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
229-230 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Leonurine is a natural alkaloid that occurs in various species of the lion's ears ( Leonotis ). Chemically leonurine is an ester of an aromatic carboxylic acid , more specifically, a syringic acid - ester .
Occurrence
Various species of the lion's ear or preparations made from them are traditionally used as herbal medicines , for example to "strengthen" the uterus, for menstrual cramps and for nervous heart problems. Leonurine and stachydrin have been found to be two effective alkaloids . With the help of modern analysis methods it has been shown that Leonurine is found in the herb of Leonurus japonicus , but not in Leonurus cardiaca or Leonotis leonurus .
synthesis
Because of its pharmacological effectiveness, a way of technical preparation of leonurine has been developed. Instead of laborious extraction from plants, it can now be obtained by reacting 4-guanidino-1-butanol with syringic acid and dicyclohexylcarbodiimide .
Pharmacological effect
In the meantime it has been scientifically proven that leonurine has an effect on the heart, as it inhibits creatine kinase . In addition, an increase in the tone of the uterine muscles in vivo and in vitro could be proven in experiments with rats . Leonurine could not establish itself as a pharmaceutical agent.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Yeung, HW; Kong, YC; Lay, WP; Cheng, KF: The Structure and Biological Effect of Leonurine in Planta Med 31 (1977) 51-56, doi : 10.1055 / s-0028-1097489 .
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A label of [No public or meaningful name is available] in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on July 7, 2020, is derived from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ R. Hegnauer: Chemotaxonomy of plants . Springer DE, 1989, ISBN 3-0348-9283-7 , pp. 611 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Kuchta, K .; Ortwein, J .; Rauwald, HW: Leonurine in Leonurus and Leonotis drugs? Detection and quantitative determination by a newly developed HPLC method In: Planta Medica 76 (2010) 12.
- ↑ Kuchta, K .; Ortwein, J .; Rauwald, HW: Leonurus japonicus, Leonurus cardiaca, Leonotis leonurus: a novel HPLC study on the occurrence and content of the pharmacologically active guanidino derivative leonurine In: Die Pharmazie 67 (2012) 973-979.
- ↑ Cheng et al .: Leonurine, an improved synthesis , In: Experientia . 1979, 35 (5): 571-2, PMID 446644 .
- ↑ Wang, Z .; Zhang PL; Ju, Y .: Effect of leonurine on the activity of creatine kinase . In: J Asian Nat Prod Res 6 (2004) 281-287.
- ^ Li, X .; Yuan, FL; Zhao, YQ; Lu, WG; Li, CW; He, CH: Effect of leonurine hydrochloride on endothelin and the endothelin receptor-mediated signal pathway in medically-induced incomplete abortion in rats in Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, pii: S0301-2115 (13) 00111-5, doi : 10.1016 / j.ejogrb.2013.02.022 .

