Machimosauridae
| Machimosauridae | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
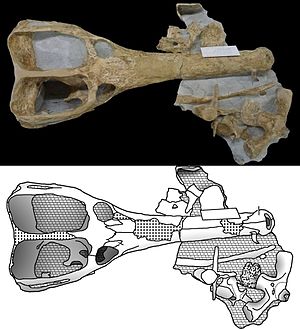
Skull of Machimosaurus buffetauti from the Upper Jurassic of Baden-Württemberg . |
||||||||||
| Temporal occurrence | ||||||||||
| Lower Jurassic ( Toarcium ) to Lower Cretaceous ( Hauterivium / Barremium ) | ||||||||||
| 182.7 to 130.7 million years | ||||||||||
| Locations | ||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||
| Machimosauridae | ||||||||||
| Jouve et al., 2016 | ||||||||||
| Subfamilies | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
The Machimosauridae are a family of extinct marine crocodiles from the Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous . Fossils come mainly from the Jurassic layers of Europe , other remains have been recovered in Africa . Some fossils from India can possibly also be assigned to the Machimosauridae. The most common fossil traditional Machimosauride is mainly from southern Germany Posidonienschiefer known Macrospondylus (formerly Steneosaurus bollensis ).
description
Like their closest relatives, the Teleosauridae , machimosaurids looked like today's gavials at first glance . Their hind legs were significantly longer than the front legs, their snout was narrow and, especially in early forms such as the Macrospondylus, still relatively long. In contrast , in many later genera such as Machimosaurus or Lemmysuchus , the snout was significantly shorter. Unlike the teleosaurids, the nostril was on the top of the tip of the snout. As with most other crocodile species , the machimosaurid body was covered with skin bone plates .
Within the subfamily Machimosaurinae, the size of the upper temporal windows increased significantly, while the number of teeth decreased. The teeth in this group of machimosaurids were characteristically blunt and formed a clearly ribbed enamel .
Machimosaurids were usually relatively large marine crocodiles. Even the early genus Macrospondylus could reach lengths of over five meters. The largest known Machimosaurid is Machimosaurus rex with an estimated length of 7.15 meters.
Systematics

Species of the Machimosauridae family have traditionally been placed in the Teleosauridae family . A rearrangement of the relationships within the Thalattosuchia meant that the Teleosauridae only includes the closest relatives of Teleosaurus , while the closest relatives of Machimosaurus with the Machimosauridae got their own family.
Teleosauridae, Machimosauridae and the genus Plagiophthalmosuchus are grouped together to form the Teleosauroidea superfamily , which is opposed to the Metriorhynchoidea superfamily . The Machimosauridae is still home to the subfamily Machimosaurinae. Within these eventually form machimosaurus , Lemmysuchus and Yvridiosuchus the tribe Machimosaurini.
Abbreviated cladogram of the Teleosauroidea according to Johnson et al . (2020):
| Teleosauroidea |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Paleoecology

Machimosaurids lived mainly in the marine habitats of the former Tethys Sea . They were found in lagoons and estuaries as well as on the high seas . Especially early machimosaurids were probably opportunists in their diet. In later machimosaurids, namely within the subfamily Machimosaurinae, a trend towards shorter snouts, pronounced jaw muscles and robust, fluted teeth can be observed. This is interpreted as adaptations to a durophage ("shell-cracking") diet. In fact, several fossils of turtles are known that appear to have been attacked by Machimosaurus .
literature
- Johnson, MM, Young, MT, & Brusatte, SL (2020). The phylogenetics of Teleosauroidea (Crocodylomorpha, Thalattosuchia) and implications for their ecology and evolution. PeerJ , 8, e9808. doi: 10.7717 / peerj.9808
- Jouve, S., Mennecart, B., Douteau, J., & Jalil, NE (2016). The oldest durophagous teleosauroid (Crocodylomorpha, Thalattosuchia) from the lower Bathonian of central High Atlas, Morocco. Palaeontology , 59 (6), 863-876. doi: 10.1111 / pala.12262
Individual evidence
- ↑ Young, MT, Hua, S., Steel, L., Foffa, D., Brusatte, SL, Thüring, S., Mateus, O., Ruiz-Omeñaca, JI, Havlik, P., Lepage, Y. & De Andrade, MB (2014). Revision of the late Jurassic teleosaurid genus Machimosaurus (Crocodylomorpha, Thalattosuchia). Royal Society Open Science , 1 (2), 140222. doi: 10.1098 / rsos.140222

