Milk shark
| Milk shark | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Captured milk sharks |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Rhizoprionodon acutus | ||||||||||||
| ( Rüppell , 1837) |
The milk shark ( Rhizoprionodon acutus ) is a species of sharp-nosed sharks ( Rhizoprionodon ) within the Requiem sharks (Carcharhinidae). The species is distributed in temperate to tropical waters of Africa, Asia and Australia near the coast. Its name is derived from the assumption in India that the consumption of the meat of this shark stimulates the milk production of breastfeeding mothers.
Appearance and characteristics
The milk shark is a medium-sized shark with an average body length of about 110 cm and a maximum length of more than 178 centimeters. He has a gray, gray-brown to violet-brown body color and a whitish belly region without pattern. The rear edges of the pectoral, ventral and anal fins as well as the lower lobe of the caudal fin are light-colored, in juveniles the fin tips and the upper caudal fin lobe are black.
The snout is long and the mouth, viewed from below, is broadly parabolic with short labial folds. The eyes are large and relatively high up on the head.
It has an anal fin and two dorsal fins . The first dorsal fin is significantly larger than the second and lies slightly in front of or over the free ends of the pectoral fins. The anal fin is slightly larger than the very small second dorsal fin and is characterized by elongated anal keels. The caudal fin has a relatively short lower and long upper lobe with a distinct end lobe. Like all species of the genus, the animals have five gill slits and no injection hole , the 4th and 5th gill slits are above the pectoral fin attachment. An interdorsal ridge is only slightly formed and therefore hardly recognizable.
Way of life
The milk shark is a shallow-water species and predatory feeds on various fish from the shore zones, and it also hunts crustaceans , snails and octopuses . The sharks are viviparous and form a yolk sac placenta ( placental viviparous ). The females get between two and five young animals with a length of about 25 to 40 cm in one litter. The animals are sexually mature when they are around two years old and around 70 cm long.
distribution
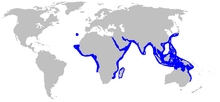
The milk shark is common in subtropical to tropical waters near the coast. It is found mainly on the coasts of Africa, South Asia, Southeast Asia and North Australia. However, the shark probably also occasionally invades the Mediterranean Sea , with only one capture of a 72 cm long female off Taranto , Italy, in 1984 documented so far . Its habitat is in the area of the continental shelf in medium water depths down to the bottom in 0 to 200 meters depth. It can also be found on sandy beaches and in estuaries .
Importance to humans
The milk shark is generally classified as harmless, as a rule it avoids encounters with swimmers and divers. It is caught and eaten relatively often, an estimate of the total number of catches or the influence on the population does not exist. There is no threat to the stocks, in the IUCN Red List it is listed as “least concern”.
supporting documents
- ↑ di Maddalena & Bänsch 2005, p. 212.
- ↑ M. Pastore, E. Tortonese: Prima segnelazione in Mediterraneo dello squalo Rhizoprionodon acutus (Ruppell). Thallasia Salentina 14, pp. 11-15; According to: de Maddalena & Bänsch 2005; P. 212
- ↑ Rhizoprionodon acutus in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2008. Posted by: CA Simpfendorfer, 2003. Retrieved on 16 May, 2009.
literature
- Leonard Compagno , Marc Dando, Sarah Fowler: Sharks of the World. Princeton Field Guides, Princeton University Press , Princeton and Oxford 2005; Pp. 317-318, ISBN 978-0-691-12072-0 .
- Alessandro de Maddalena, Harald Bänsch: Sharks in the Mediterranean, Franckh-Kosmos Verlags-GmbH, Stuttgart 2005; Pages 211-212, ISBN 3-440-10458-3 .
Web links
- Milky shark on Fishbase.org (English)