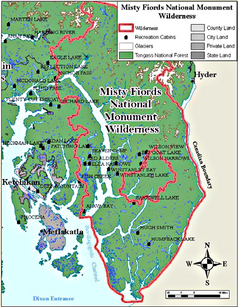
Misty Fjords National Monument
| Misty Fjords National Monument | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mouth of one of the fjords | ||
|
|
||
| Location: | Alaska , United States | |
| Specialty: | Coastal mountains with deep fjords | |
| Next city: | Ketchikan | |
| Surface: | 9,284.9 km² | |
| Founding: | December 1, 1978 | |
Misty Fjords National Monument is a nature reserve of the type of a national monument in the southeast of the US state Alaska. By far the largest national monument in the United States in terms of area, it encompasses the tip of the Alaska Panhandle , the southernmost part of Alaska. It is characterized by the coastal mountains of the Boundary Ranges , which are cut by deep fjords and overgrown with rainforest of the temperate latitudes .
The reserve lies entirely in the Tongass National Forest , a National Forest , and how it is from the US Forest Service managed. It was established in 1978 by US President Jimmy Carter under the name "Misty Fiords National Monument" and confirmed in 1980 by the Congress of the United States in the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act under the current spelling. Almost its entire area was placed under further protection as the Wilderness Area as Misty Fjords National Monument Wilderness .
description
Most of the reserve is on the mainland in the mountains of the Boundary Ranges, between the Portland Canal in the east and the Behm Canal in the west. The Portland Canal and the ridge of the mountain range form the border of the reserve and Alaska with the Canadian province of British Columbia . To the north, Salmon Glacier , North America's fifth largest glacier, extends from Canada across the border and into the National Monument. To the west, a strip of Revillagigedo Island is part of the reserve.
The mountains of the area consist of granite , which has been carved out by glaciers mainly into round peaks and deep trough valleys . Due to tectonic subsidence and the rise in sea level after the last ice age (known as Wisconsin glaciation in North America ), the valley floors are now up to 300 m below sea level and the valleys have become fjords. The steep walls typically rise between 600 and 900 m above water, and various waterfalls plunge from hanging valleys . The highest falls from Big Goat Lake 300 m deep into Wilson Lake . Due to the comparable granite, the similar geological formation and other similarities, the Californian naturalist and philosopher John Muir compared the fjords that he saw on his travels between 1879 and 1899 with the Yosemite Valley in California's Sierra Nevada .
The mountain range receives annual rainfall of a little over 4000 mm from uphill rain, the forests on the slopes are therefore qualified as rainforests. The characteristic tree species of the area is the Sitka spruce , along with the Western American hemlock , rock fir , purple fir and the giant tree of life . Deciduous trees are rarer, the western balsam poplar grows in sheltered areas .
The animal world is almost unaffected by human influences. Grizzly bears and American black bears , wolves , elks , mountain goats and mule deer as well as spruce martens , new world otters and wolverines live in the reserve . Five species of salmon inhabit the area's rivers and inlets.
Visits
Misty Fjords National Monument is difficult to access for visitors. There is no road connection. Cruise ships make regular trips to the Behm Canal, the reserve can also be reached on day trips from Ketchikan by catamaran or on excursions by seaplane . A view of the mountains and the fjords is also provided by the ferry ships on the Alaska Marine Highway , which pass the west coast of the National Monument on the Inside Passage .
The protected area is an excellent area for sea kayaking , with a tidal range of up to 7.50 m . The Forest Service rents 14 log cabins on the coast and larger lakes, and some hiking trails are rudimentary in their vicinity. Visitors to the huts must be flown in.
Conservation and Conflict
Due to the wilderness character and the remoteness of the area, only a few protective measures are required. In the areas regularly visited by visitors, the rangers of the Forest Service sporadically search for neophytes , alien plant species introduced by humans. In addition, stretches of path that have been walked on are secured in such a way that no landslides occur in streams that could become silted up by the entry, which would damage them as spawning grounds for fish.
The high frequency of seaplanes over the area and the number of landings on lakes in the wilderness reserve are problematic. In the most attractive parts of the landscape, the noise from overflights and the frequency of encounters with people and human influences have a negative effect on the experience of "loneliness, seclusion and undisturbed relaxation".
In 1980, when it was placed under additional protection as a wilderness reserve, a central part of the monument around Quartz Mountain was excluded because it is believed to have the largest occurrence of molybdenum on earth. The deposit has not yet been used, but should not be ruled out either.
Web links
- US Forest Service: Misty Fjords National Monument (official site )
- Wilderness.net: Misty Fjords National Monument Wilderness (English)
supporting documents
- ^ Presidential proclamation 4623 , December 1, 1978
- ^ John Muir, Travels in Alaska , Boston, New York, Houghton Mifflin Co., 1915, p 45
- ^ Tongass National Forest - Monitoring Report 2006
- ↑ Alaska History and Cultural Studies ( Memento of the original from May 13, 2006 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.